* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exercise 17 - Harford Community College
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
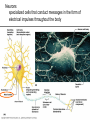
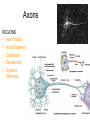
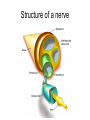
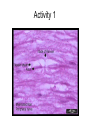
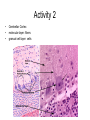
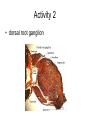
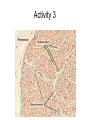
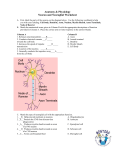
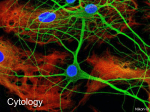
Exercise 17 Marieb & Mitchell page 257 Neurons specialized cells that conduct messages in the form of electrical impulses throughout the body “typical” neuron components • SOMA – also called the perikaryon – major biosynthetic center containing the usual organelles except for centrioles • Dendrites – cell processes that are the receptive regions of the cell • Axon – generates and conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body to the axon terminals – myelin sheath – whitish, fatty, segmented covering – protects, insulates, and increases conduction velocity Axons do not have Nissl bodies or Golgi apparati Axons REGIONS • Axon Hillock • Initial Segment • Collaterals • Telodendria • Synaptic Terminals Glia of the CNS astrocytes – maintain blood-brain barrier – provide structural framework for brain due to extensive cytoskeleton – repair damaged neural tissue – guide neuronal development – regulating interstitial environment Glia of the CNS ependymal cells – line the central cavities of the brain and spinal cord – help circulate cerebrospinal fluid oligodendrocytes – wrap around axons to form myelin sheaths Glia of the CNS microglia – least numerous and smallest CNS cells – patrol CNS as “immune” cells Glia of the PNS satellite cells • found surrounding neuron cell bodies within ganglia Schwann cells • surround nerve fibers, sometimes form myelin sheath Structure of a nerve Activities • Do activities 1-3 and then we will go over the questions and look at some representative pictures. Activity 1 Activity 1 Activity 2 • • • Cerebellar Cortex molecular layer: fibers granual cell layer: cells Activity 2 • Cerebral Cortex: Pyramidal Cells Activity 2 • dorsal root ganglion Activity 3