* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Signal Processing in Single Cells
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
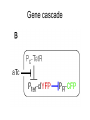
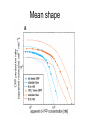
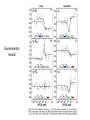
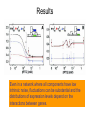
Signal Processing in Single Cells Tony 03/30/2005 The Question How signals are transmitted through gene cascades in noisy cellular environments? Work by Rosenfeld et al • Gene Regulation Function (GRF) – The relation between the concentration of active transcription factors in a cell and the rate at which their downstream gene products are produced through transcription and translation. • Three fundamental aspects of GRF to study: – Mean shape – Typical deviation from this mean – Time scale over which such fluctuations persist Gene cascade Experimental tricks • Regulator dilution method • Relative fluorescence intensity of individual protein molecules apparent number of molecules per cell. • Hill function Mean shape Fluctuations • After normalizing production rates to the average cellcycle phase, substantial variation still remains in the production rates, and their standard deviation is ~40% of the mean GRF. • Intrinsic noise – Results from stochasticity in the biochemical reactions at an individual gene and would cause identical copies of the same gene to express at different levels. – ~20% of the total noise • Extrinsic noise – Originates from fluctuations in cellular components such as metabolites, ribosomes, and polymerases. – Contributes a variation in protein production rates of ~35%. Time scales of the fluctuations Conclusions • Slow fluctuations give the genetic circuits memory, or individuality, lasting roughly one cell cycle. They present difficulty for modeling genetic circuits. • There is thus a fundamental tradeoff between accuracy and speed in purely transcriptional responses. Accurate cellular responses on faster time scales are likely to require feedback from their output. Work by Pedraza & Oudenaarden • Expression correlations between genes in single cells were measured. • A model was developed that explains the complex behavior exhibited by the correlations and reveals the dominant noise sources. Gene cascade Experimental results Model Model • Langevin approach • Noise terms: – Intrinsic noise at specific gene – Transmitted intrinsic noise from the upstream genes • The Intrinsic noise for upstream gene • The effect of temporal averaging • The susceptibility of downstream gene to upstream gene (logarithmic gain) – Global noise modulated by the network • The direct effect on the gene • The transmitted effect from upstream genes • The effect of the correlated transmission Results Even in a network where all components have low intrinsic noise, fluctuations can be substantial and the distributions of expression levels depend on the interactions between genes.