* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Here - Stanford University
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Myron Ebell wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Saskatchewan wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Canada wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
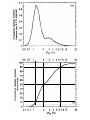
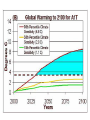
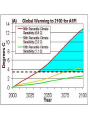
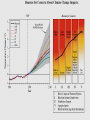
Global Climate Alteration: A Survey of the Science and Policy Implications D. Warner North (presenter), replacing Stephen H. Schneider, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA Congress on Energy Policy and Climate Alteration, Stuttgart, Germany October 11, 2004 Website References • Professor Stephen H. Schneider: http://stephenschneider.stanford.edu/ • Dr. and Consulting Professor, D. Warner North: http://www.northworks.net/w_main.htm Article 2 of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) states that: “The ultimate objective of this Convention and any related legal instruments that the Conference of the Parties may adopt is to achieve, in accordance with the relevant provisions of the Convention, stabilization of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system”. The Framework Convention on Climate Change further suggests that “Such a level should be achieved within a time frame sufficient to allow ecosystems to adapt naturally to climate change, to ensure that food production is not threatened and to enable economic development to proceed in a sustainable manner.” US National Academies Reports • National Research Council Report, for the White House (2001): Climate Change Science: An Analysis of Some Key Questions http://books.nap.edu/catalog/10139.html • Policy Implications of Greenhouse Warming, NaRC report (1991): http://books.nap.edu/catalog/1794.html • Confronting Climate Change: Strategies for Energy Research and Development, NaRC report, 1990 http://books.nap.edu/catalog/1600.html National Academies, 2001 Greenhouse gases are accumulating in Earth's atmosphere as a result of human activities, causing surface air temperatures and subsurface ocean temperatures to rise. Temperatures are, in fact, rising. The changes observed over the last several decades are likely mostly due to human activities, but we cannot rule out that some significant part of these changes is also a reflection of natural variability. Humaninduced warming and associated sea level rises are expected to continue through the 21st century. Secondary effects are suggested by computer model simulations and basic physical reasoning. These include increases in rainfall rates and increased susceptibility of semiarid regions to drought. The impacts of these changes will be critically dependent on the magnitude of the warming and the rate with which it occurs. - First paragraph of report prepared in three weeks at the request of the Bush White House (p. 1, http://books.nap.edu/catalog/10139.html) Books on Climate Variability Brian M. Fagan, – The Long Summer: How Climate Changed Civilization (12,000 years ago – present) – The Little Ice Age (1000 years ago – present) Range of Expert Opinion Source: Morgan and Keith, ES&T, 1995 (on Schneider Website) Impacts on California “Emissions pathways, climate change, and impacts on California,” by Stephen H. Schneider and 18 co-authors, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 101(34):12422-12427, August 24, 2004 http://www.pnas.org/cgi/contents/full/101/34/12422 US Government: Climate Change Science Program • Director: James R. Mahoney • Our Changing Planet: The U.S. Climate Change Science Program for Fiscal Years 2004 -2005, August 2004: http://www.usgcrp.gov/usgcrp/Library/ocp2 004-5/default.htm CCSP Report, Aug 2004 “Climate variability and change can profoundly influence social and natural environments throughout the world, with consequent impacts on natural resources and industry that can be large and far-reaching. … Recent advances in climate science are providing information for decisionmakers and resource managers to better anticipate and plan for potential impacts of climate variability and change. Further advances will serve the nation by providing improved knowledge to enable more scientifically informed decisions across a broad array of climate-sensitive sectors.” - “Our Changing Planet,” p. 42 http://www.usgcrp.gov/usgcrp/Library/ocp2004-5/ocp2004-5.pdf From Climate Change Science to Policy • Policy decisions must be made under uncertainty! • Benefits from reducing reliance on oil and coal: – reduce CO2 emissions and rate of atmospheric increase – reduce demand, and therefore price, for oil – reduce air pollution and health impacts from coal combustion – reduce turmoil in Middle East • Industrialization and economic growth of China, India, etc. will increase demand for oil, CO2 emissions 1991 National Academies Report Recommendation “Despite the great uncertainties, greenhouse warming is a potential threat sufficient to justify action now. Some current actions could reduce the speed and magnitude of greenhouse warming; others could prepare people and natural systems of plants and animals for future adjustments to the conditions likely to accompany greenhouse warming.” National Research Council, 1991, p. 72 http://books.nap.edu/catalog/1794.html