* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate and Atmospheric Changes
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
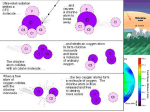
OZONE DEPLETION & CLIMATE CHANGE (Ch 20) ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM UV – A (AGING): Low energy. Thought to contribute to premature aging and wrinkling of the skin and has recently been implicated as a cause of skin cancer. UV – B (BURNING): Medium energy. UVB is more dangerous than UVA and has been implicated as a major cause of skin cancers, sunburning and cataracts. UV – C: High energy. UVC is extremely dangerous but does not reach the earth’s surface due to absorption in the atmosphere. Most of the radiation below 290 nm is absorbed by the ozone in the upper atmosphere. Depletion of this layer increases the amount of UVC reaching ground level. TYPES OF UV RADIATION HEALTH OZONE LAYER DECREASES…. INCREASED UV RADIATION ENTERS Decreased primary productivity (land & ocean) Damage to fish/amphibians / mammals Disrupt food chain Effects on food crops (beans, wheat, rice, corn) IMPACTS ON ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS ATMOSPHRE LAB Cumulative Graph should look like… OZONE DEPLETION Ozone- molecule consisting of 3 oxygen atoms Benefit to humans because it absorbs harmful UV radiation Ozone layer is being depleted because of the addition of chemicals (esp. CFC’s) that break apart the ozone molecule OZONE VIDEO (2:20) CHEMICAL CLASSES OF OZONE DESTROYERS CHLOROFLOUROCARBONS (CFC'S) HALOCARBONS/HALONS (ODS) No significant natural Highly reactive group 17 sources identified Source: Air conditioning, Aerosol propellants, solvents, styrofoam GREAT longevity takes 5-7 years for CFC’s to go from ground to upper atm. Cl, Br, F Sources: Styrofoam, Solvents, Soil Fumigant, Fire Extinguishers OZONE PHLEMISTRY WKST O2 becomes O3 1)O2 + UV ●O + ●O 2) O2 + ●O O3 O3 becomes O2 1)O3 + UV O2 + ●O 2) O3 + ●O O2 + O2 CFCs degrades O3 into O2 1)CCl2F2 + UV ●CClF2 + ●Cl 2) ●Cl + O3 ClO● + O2 NO degrades O3 into O2 1) NO + O3 NO2 + O2 AIRPLANES! OZONE CHEMISTRY for the visual learners STEP 1: NATURAL FORMATION OF OXYGEN STEP 2: Natural Formation of Ozone in the STRATOSPHERE Step 3: Natural Breakdown of Ozone in the STRATOSPHERE STEP 4: CFC’s BREAKING DOWN OZONE (anthropogenic causes) Free Radical Chlorine CFC OZONE Oxygen Free Radical Oxygen CLO* PER CHLORINE ATOM BROKEN OFF BY UV RADIATION FROM CFC’S, 100-300,000 OZONE MOLECULES CAN BE BROKEN DOWN (~900,000 O3 MOLEUCLES PER CFC!) Ozone over Antarctica ANTARCTIC OZONE HOLE (16 MIN) OZZY OZONE (10 MIN) THOMAS MIDGLEY CLIMATE CHANGE Long-term change in the earth's climate, especially a change due to an increase in the average atmospheric temperature. CLIMATE CHANGE - GLOBAL WARMING GLOBAL WARMING OR CLIMATE CHANGE? GLOBAL WARMING INDICATES THAT THE GLOBAL TEMPERATURE IS INCREASING AND IT IS GETTING HOTTER EVERYWHERE. CLIMATE CHANGE INDICATES THAT CLIMATES ARE SHIFTING AND UNCHARACTERISTIC WEATHER PATTERNS WILL ARISE WHEATHER THAT IS HOTTER OR COOLER, WETTER OR DRYER. There is absolutely ZERO debate that global temperatures have gone up and down for centuries GREENHOUSE EFFECT Causes of Climate Change Description of what it is Explanation of how it impacts climate (What SCIENTISTS say) Volcanic eruptions When volcanoes erupt, they release dissolved gases (like carbon dioxide, water vapor and sulfur dioxide) into the atmosphere Adds to the build-up of Greenhouse Gases Sunspots More emitted radiation and increased More sunspots will increase the amount temperatures are found around sunspots of heat that stays within the atmosphere. Earth’s orbit There is variation in Earth’s tilt which affects the amount of solar radiation received. Depending on the season, more or less energy is received from the sun. Carbon Dioxide fluctuations As heat is reflected back out into space, carbon dioxide (CO2) absorbs some of the heat. Heat is retained in the atmosphere (not radiated back into space) causing the global temperature to rise. TRENDS IN ATMOSPHERIC CO2 Effects of Climate Change Link: The Nature Conservancy 1. HIGHER TEMPERATURES The five hottest years on record have all occurred since 1997. 2. CHANGING LANDSCAPES Changing patterns of rain and snow are forcing trees and plants around the world to move toward polar regions and up mountain slopes ALASKA - Portage Glacier 1914 2004 ARIZONA- Colorado River June 2002 Dec 2003 Effects of Climate Change 3. WILDLIFE AT RISK Rising temperatures are changing weather and vegetative patterns across the globe, forcing animal species to migrate to new, cooler areas in order to survive. 4. RISING SEAS Experts predict that 1/4 of Earth’s species will be headed for extinction by 2050 Sea level rise from climate change could displace tens of millions of people. Sea levels could continue to rise between 4 inches and 36 inches over the next 100 years. Effects of Climate Change 5. INCREASED RISK OF DROUGHT, FIRE & FLOODS Massive land erosion is one result of overgrazing & drought in Kenya 6. STRONGER STORMS & HURRICANES Hurricanes and tropical storms to become more intense — lasting longer, unleashing stronger winds, and causing more damage to coastal ecosystems Effects of Climate Change 7. MORE HEAT RELATED ILLNESS & DISEASE As temperatures rise, so do the risks of heat-related illness and even death for the most vulnerable human populations. Increase the spread of infectious diseases. 8. ECONOMIC LOSSES Climate change could cost between 5 and 20 percent of the annual global gross domestic product. Declining crop yields could put hundreds of thousands of people at risk for starvation. Effects of Climate Change 9. OCEAN ACIDIFICATION As temperatures rise, so does the amount of carbon dioxide in the ocean causing acidic water. 10. EL NINO & LA NINA Weather patterns in the Pacific Ocean change causing an increased frequency of bad weather events to occur around the world. Global Atmospheric Concentration of CO2 CLIMATE CHANGE CONTROVERSY? NOT FOR SCIENTISTS! My personal opinion The way I see it…. WHAT CAN YOU DO TO HELP SLOW DOWN GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE? Neil deGrasse Tyson, Astronomer makes a very good point... 1000 Years of CO2 & Global Warming Temperature (Northern Hemisphere) Year Year 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 Parts Per Million Degree Celsius Increase CO2 Concentrations Billions of Metric Tons Carbon Goal: Reductions in 2007 CO2 Per Year of Metric Billions CarbonTons Carbon Gigaton Our Goal 2007 Reductions in CO2 Per Year Produce electricity efficiently Use electricity efficiently Vehicle efficiency Solar and Wind Power Biofuels Carbon capture and storage How ozone is destroyed by CFCs