* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint Presentation - Global Change Curricula and
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Myron Ebell wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Saskatchewan wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
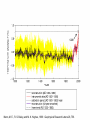
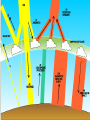
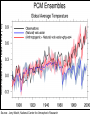
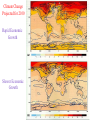
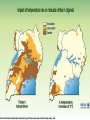
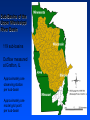
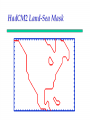
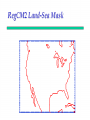
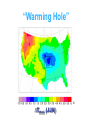
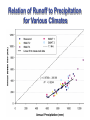
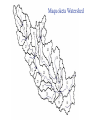
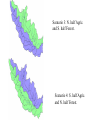
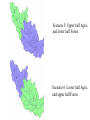
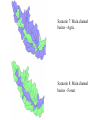
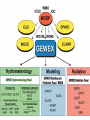
Regional Climate Modeling: A Tool for Decision-Makers Eugene S. Takle Agronomy Department Geological and Atmospheric Science Department Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 50011 [email protected] Institute for Science and Society Iowa State University 4 May 2004 PROJECT TO INTERCOMPARE REGIONAL CLIMATE SIMULATIONS Outline Evidence for global climate change Future atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations Simulations of global climate and future climate change Implications for stream flow and nutrient loss International collaboration for understanding water and energy cycles Summary PROJECT TO INTERCOMPARE REGIONAL CLIMATE SIMULATIONS Carbon Dioxide and Temperature Carbon Dioxide and Temperature 2004 Carbon Dioxide and Temperature 2040 2004 Carbon Dioxide and Temperature Stabilization at 550 ppm Carbon Dioxide and Temperature “Business as Usual” (fossil intensive) 2100 Associated Climate Changes Global sea-level has increased 1-2 mm/yr Duration of ice cover of rivers and lakes decreased by 2 weeks in N. Hemisphere Arctic ice has thinned substantially, decreased in extent by 10-15% Reduced permafrost in polar, sub-polar, mountainous regions Growing season lengthened by 1-4 days in N. Hemisphere Retreat of continental glaciers on all continents Poleward shift of animal and plant ranges Snow cover decreased by 10% Earlier flowering dates Coral reef bleaching Source: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 2001 Report PROJECT TO INTERCOMPARE REGIONAL CLIMATE SIMULATIONS Mann, M. E., R. S. Bailey, and M. K. Hughes, 1999: Geophysical Research Letters 26, 759. PROJECT TO INTERCOMPARE REGIONAL CLIMATE SIMULATIONS PROJECT TO INTERCOMPARE REGIONAL CLIMATE SIMULATIONS Source: Jerry Meehl, National Center for Atmospheric Research Source: National Center for Atmospheric Research Source: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 2001 Report 40% Probability 5% Probability Source: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 2001 Report Climate Change Projected for 2100 Rapid Economic Growth Slower Economic Growth IPCC Summary for Policy Makers An increasing body of observations gives a collective picture of a warming world and other changes in the climate system Emissions of greenhouse gases and aerosols due to human activities continue to alter the atmosphere in ways that are expected to affect the climate IPCC Summary for Policy Makers, cont’d Confidence in the ability of models to project future climate has increased There is new and stronger evidence that most of the warming observed over the last 50 years is attributable to human activities IPCC Summary for Policy Makers, cont’d Confidence in the ability of models to project future climate has increased There is new and stronger evidence that most of the warming observed over the last 50 years is attributable to human activities IPCC Summary for Policy Makers, cont’d Confidence in the ability of models to project future climate has increased There is new and stronger evidence that most of the warming observed over the last 50 years is attributable to human activities IPCC Summary for Policy Makers, cont’d Anthropogenic climate change will persist for many centuries Further action is required to address remaining gaps in information and understanding http://www.grida.no/climate/vital/38.htm Climate Surprises Breakdown of the ocean thermohaline circulation (Greenland melt water) Breakoff of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet PROJECT TO INTERCOMPARE REGIONAL CLIMATE SIMULATIONS Antarctica Greenland 0 Cold Warm Climate Regional Climate Change for the US Midwest Observed and projected changes in climate Impact on water quantity and water quality Policy implications PROJECT TO INTERCOMPARE REGIONAL CLIMATE SIMULATIONS For the Midwest Warming will be greater for winter than summer Warming will be greater at night than during the day A 3oF rise in summer daytime temperature triples the probability of a heat wave Growing season will be longer (8-9 days longer now than in 1950) More precipitation Likely more soil moisture in summer More rain will come in intense rainfall events Higher stream flow, more flooding Sub-Basins of the Upper Mississippi River Basin 119 sub-basins Outflow measured at Grafton, IL Approximately one observing station per sub-basin Approximately one model grid point per sub-basin Soil Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) Long-term, continuous watershed simulation model (Arnold et al,1998) Assesses impacts of climate and management on yields of water, sediment, and agricultural chemicals Physically based, including hydrology, soil temperature, plant growth, nutrients, pesticides and land management Daily time steps PROJECT TO INTERCOMPARE REGIONAL CLIMATE SIMULATIONS SWAT Output with Various Sources of Climate Input Validation of SWAT: Annual Stream Flow at Grafton, IL Validation of SWAT: Monthly Stream Flow at Grafton, IL RegCM2 Simulation Domain Red = global model grid point Green/blue = regional model grid points Annual Stream Flow Simulated by SWAT Driven by the RegCM2 Regional Climate Model with NNR Lateral Boundary Conditions Mean Monthly Precipitation Simulated by the RegCM2 Regional Climate Model with NNR Lateral Boundary Conditions Seasonal Stream Flow Simulated by SWAT Driven by the RegCM2 Regional Climate Model with NNR Lateral Boundary Conditions “Warming Hole” ˚C DTmax (JJA) Ten-Year Mean Precipitation Generated by the RegCM2 Regional Climate Model Driven with HadCM2 Global Model Results for the Contemporary and Future Scenario (2040s) Climate Ten-Year Mean Monthly Stream Flow Generated by the RegCM2 Regional Climate Model Driven with HadCM2 Global Model Results for the Contemporary and Future Scenario (2040s) Climate Comparison of Simulated Stream Flow under Climate Change with Various Model Biases Relation of Runoff to Precipitation for Various Climates Regional Climate Modeling for Informing Policy on Water Quality How does the combination of climate change and land use impact water quality? Use nitrates and sediment as indicators What alternative land management strategies will improve water quality? What policies need to be implemented to achieve this water quality improvement? PROJECT TO INTERCOMPARE REGIONAL CLIMATE SIMULATIONS Maquoketa Watershed Scenario 1: all Agriculture Scenario 2: all Forest Scenario 3: N. half Agric. and S. half Forest. Scenario 4: S. half Agric. and N. half Forest. Scenario 5: Upper half Agric. and lower half Forest. Scenario 6: Lower half Agric. and upper half Forest. Scenario 7: Main channel basins - Agric. Scenario 8: Main channel basins - Forest. Fractional changes in mean annual flow and yield under various scenarios normalized by the fractional change in area from all-agricultural for the scenario. Scenario 1995 (normal year) 1993 (wet year) 1988 (dry year) Flow Sediment yield Nitrate Scenario 1 - - - Scenario 2 -0.01 1.00 0.99 Scenario 3 -0.02 0.42 0.52 Scenario 4 0.00 0.55 0.48 Scenario 5 -0.03 0.75 0.60 Scenario 6 0.03 0.21 0.40 Scenario 7 -0.02 0.68 0.74 Scenario 8 0.02 0.28 0.25 Fractional changes in mean annual flow and yield under various scenarios normalized by the fractional change in area from all-agricultural for the scenario. Scenario 1995 (normal year) 1993 (wet year) 1988 (dry year) Flow Sediment yield Nitrate Scenario 1 - - - Scenario 2 -0.01 1.00 0.99 Scenario 3 -0.02 0.42 0.52 Scenario 4 0.00 0.55 0.48 Scenario 5 -0.03 0.75 0.60 Scenario 6 0.03 0.21 0.40 Scenario 7 -0.02 0.68 0.74 Scenario 8 0.02 0.28 0.25 Improving Regional Climate Models Project to Intercompare Regional Climate Simulations Transferability Working Group of GEWEX PROJECT TO INTERCOMPARE REGIONAL CLIMATE SIMULATIONS Project to Intercompare Regional Climate Simulations (PIRCS) PIRCS Mission To provide a common framework for evaluating strengths and weaknesses of regional climate models and their component procedures through systematic, comparative simulations PIRCS Co-Directors Ray Arritt [email protected] Bill Gutowski [email protected] Gene Takle [email protected] http://www.pircs.iastate.edu/ PROJECT TO INTERCOMPARE REGIONAL CLIMATE SIMULATIONS PIRCS Participating Groups Danish Met. Inst. (HIRHAM4; J.H. Christensen, O.B. Christensen) Université du Québec à Montréal (D. Caya, S. Biner) Scripps Institution of Oceanography (RSM; J. Roads, S. Chen) NCEP (RSM; S.-Y. Hong) NASA - Marshall (MM5/BATS; W. Lapenta) CSIRO (DARLAM; J. McGregor, J. Katzfey) Colorado State University (ClimRAMS; G. Liston) Iowa State University (RegCM2; Z. Pan) Iowa State University (MM5/LSM; D. Flory) Univ. of Maryland / NASA-GSFC (GEOS; M. Fox-Rabinovitz) SMHI / Rossby Centre (RCA; M. Rummukainen, C. Jones) NOAA (RUC2; G. Grell) ETH (D. Luethi) Universidad Complutense Madrid (PROMES; M.Gaertner) Université Catholique du Louvain (P. Marbaix) Argnonne National Lab (MM5 V3; J. Taylor, J. Larson) St. Louis University (Z. Pan) PROJECT TO INTERCOMPARE REGIONAL CLIMATE SIMULATIONS La Plata Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment OBJECTIVES • Determine the hydrological cycle and energy fluxes by means of global measurements of observable atmospheric and surface properties. • Model the global hydrological cycle and its impact on the atmosphere, oceans, and on the land surface. • Develop the ability to predict the variations of global and regional hydrological processes and water resources, and their response to environmental change. • Foster the development of observing techniques, data management, and assimiliation systems suitable for operational application to long-range weather forecasts, hydrology, and climate predictions. Phase II Primary Science Questions Updated GEWEX Science Questions : 1. Are the Earth’s Energy Budget and Water Cycle Changing? Is the Water Cycle Accelerating? 2. How do Processes Contribute to Feedback and Causes of Natural Variability? 3. Can We Predict these Changes on up to S - IA? 4. What are the Impacts of these Changes on Water Resources? Data Management Water and Energy Budget Studies GAME Water Resource Applications Project Sources and Cycling of Water Extremes Predictability Transferability CEOP IAEA Summary Regional climate models demonstrate sufficient skill to be useful for driving some climate impacts assessment models for the purpose of informing policy makers and decision-makers of vulnerabilities and opportunities associated with future climate change PROJECT TO INTERCOMPARE REGIONAL CLIMATE SIMULATIONS For More Information See my online Global Change course: http://www.meteor.iastate.edu/gccourse Contact me directly: [email protected] PROJECT TO INTERCOMPARE REGIONAL CLIMATE SIMULATIONS