* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GGP3015 CLIMATIC CHANGE: Recent and future
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Canada wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
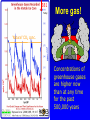
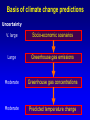
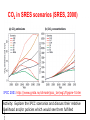
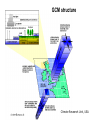
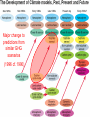
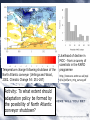
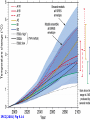
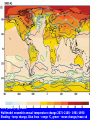
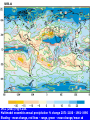
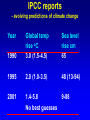
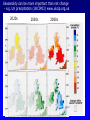
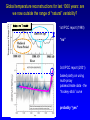
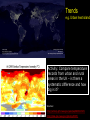
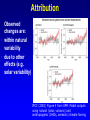
Demystifying global warming Some basic observations for international students JN Birchall ‘Global Warming Update’, • The greenhouse effect • Making predictions … and some possible surprises • What are the predictions? • Past trends in climate • Debates on the ‘climate change’ problem • Policy advice Supplementary materials: • Exercise on observations of recent climate change • Information sources and ideas The greenhouse effect 381 More gas! ‘Natural’ CO2 conc. Concentrations of greenhouse gases are higher now than at any time for the past 500,000 years Making predictions • • • • • How are predictions made? What are the sources of uncertainty? Can we trust climate models? What factors do models include? Are there major sources of uncertainty not accounted for? Basis of climate change predictions Uncertainty V. large Socio-economic scenarios Large Greenhouse gas emissions Moderate Greenhouse gas concentrations Moderate Predicted temperature change CO2 in SRES scenarios (SRES, 2000) IPCC 2001 http://www.grida.no/climate/ipcc_tar/wg1/figspm-5.htm Activity: Explore the IPCC scenarios and discuss their relative likelihood and/or policies which would see them fulfilled GCM structure Climate Research Unit, UEA One way to test a climate model: Comparing observed climate with modeled climate IPCC (2001): Figure 8.2 lower left Major change to predictions from similar GHG scenarios (1996 cf. 1990) Some possible surprises…. • Methane hydrates (oceans 9500 Gt, permafrost 400 Gt) • Carbon cycle: strength of ocean and terrestrial ‘sinks’ • Ocean circulation: the ‘thermohaline conveyor’ Methane hydrates stored in oceans and permafrost Activity: If 10% of methane hydrates were released, how does this compare with anthropogenic sources? NASA Earth Observatory http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Newsroom/NasaNews/2001 /200112106303.html Will natural sinks persist? Activity: Evaluate the impact of the decrease/loss of the oceanic and/or terrestrial carbon sink on global carbon flux Woods Hole research Center (2004) http://www.whrc.org/carbon/missingc.htm Temperature change following shutdown of the North Atlantic conveyor (Vellinga and Wood, 2002. Climatic Change 54: 251-267) Activity: To what extent should adaptation policy be formed by the possibility of North Atlantic conveyor shutdown? Likelihood of decline in MOC - from a survey of scientists in the RAPID programme http://www.soc.soton.ac.uk/rapi d/sci/pdf/ann_mtg_survey.pdf What are the predictions? • Range • Regional patterns • Changing ideas • Seasonality IPCC(2001) Fig 9.14 IPCC (2001) Fig 9.10d. Multimodel ensemble annual temperature change 2071-2100 - 1961-1990 Shading - temp change, Blue lines - range oC, green - mean change/mean sd IPCC (2001) Fig 9.11d. Multimodel ensemble annual precipitation % change 2071-2100 - 1961-1990 Shading - mean change, red lines - range, green - mean change/mean sd IPCC reports - evolving predictions of climate change Year 1990 Global temp rise oC 3.0 (1.5-4.5) Sea level rise cm 65 1995 2.0 (1.0-3.5) 48 (13-94) 2001 1.4-5.8 No best guesses 9-88 Seasonality can be more important than net change - e.g. UK precipitation (UKCIP02) www.ukcip.org.uk 2020s 2050s 2080s Past trends in climate • Is there a trend in global climate change? • How do current temperatures compare with those in the past? Frost fair on the River Thames (1814) How much has global temperature risen over the past 100 years? Timing of IPCC report preparation 1994 2000 1989 Activity(s): Are current trends in climate consistent with predictions for the future? See file. Global temperature reconstructions for last 1000 years: are we now outside the range of “natural” variability? 1st IPCC report (1990) “no” 3rd IPCC report (2001) based partly on using multi-proxy palaeoclimate data - the “hockey-stick” curve probably “yes” Is the hockey stick still valid? Multiple “spaghetti curves” now published • larger changes than original hockey stick • still show the late C20th as the warmest period of the last millennium • how critical is this anyway to the case for human-induced warming? DEBATES • There is genuine broad (although not 100%) consensus in the climate science community on main issues • Argument, scepticism and hypothesis testing are at the heart of good science • Publication of research, review and quality control are essential in this process Arguments of ‘climate sceptics’ • Trends. There is no significant trend in global temperature (e.g. urban heat island effect, geographic coverage of data) • Attribution. Human activities are not responsible for observed trends • Impacts. The negative impacts of predicted climate change are overestimated; cost-benefit analysis does not support mitigation action Trends e.g. Urban heat island Activity: Compare temperature records from urban and rural areas in the UK – is there a systematic difference and how big is it? Sources: http://antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov/apod/ap040822.html http://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp/2005/ Attribution Observed changes are: • within natural variability • due to other effects (e.g. solar variability) IPCC (2001) Figure 4 from SPM. Model outputs using natural (solar, volcanic) and anthropogenic (GHGs, aerosols) climate forcing Impacts sceptics The costs of mitigating climate change are greater than the benefits gained from adapting to change Best exemplified by Bjorn Lomborg in ‘the skeptical environmentalist’ Activities: How accurate are estimates of costs and benefits likely to be? Economic costing does not include costs to natural systems – does this matter? Science, consensus and debate Supporter Consensus Sceptic Contrasting reading - Fact vs fiction? Is the distinction clear? Activity: Take extracts from the above (or use www sites) and identify differences in style, language, use of documentation, nature of documentation International policy – is scientific advice followed? International policy Scientific advice Media and public opinion Pressure groups (±) Government delegates International policy Acceptance in national governments Government policy .. and action Activity: Follow one of the COP meetings linked to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change www.unfccc.org What are ‘desirable’ levels of future climate change? Defined by: • Global temperature (+2oC?) • Global emissions (2.5 Gt C fossil fuels pa?) • Atmospheric concentration (450-550 ppm CO2?) • Timescale e.g. UK RCEP (2002) Suggest 60% reduction on 1990 CO2 emissions by 2050 for UK Compare with: – Kyoto target of c. 5.2% by 2008-2012 for Annex 1 countries – UK Government target of 20% by 2010 (and may hit 10%....) Use the graph below from the RCEP Energy report as a starting point for debating questions such as: Which parts of the world are the biggest contributors to climate change? Should targets for reductions be based on current total contributions, per capita emissions or perhaps emissions per GDP?