* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download monera - Sumber Belajar
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Lipopolysaccharide wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
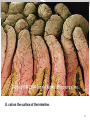
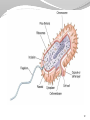
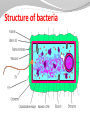
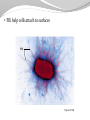
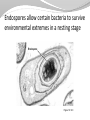
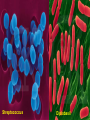
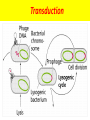
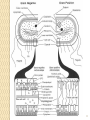
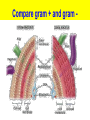
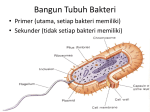
1 The "six" kingdom taxonomic scheme 2 What do you think about………….. TBC Prokaryotes are classified into two groups : • Founded by Anthony van Leeuwenhoek (1674). •bacterium named by Ehrenberg (1828), from Yunani word is βακτηριον meaning "small stick". E. coli on the surface of the intestine. 6 E. coli on the surface of human skin 7 Kingdom Archaebacteria Found in harsh environments (undersea volcanic vents, acidic hot springs, salty water) Cell walls without peptidoglycan Plasma membrane contain lipid with eter bound Ribosom contain some RNA Polymerase Subdivided into 3 groups based on their habitat -1. methanogens, 2. thermoacidophiles, & 3. extreme halophiles Archaea live in anaerobic swamps salt lakes acidic hot springs deep-sea hydrothermal vents animal digestive systems Kingdom Eubacteria (true bacteria) Cell walls with peptidoglycan Ribosom contain one kind of RNA Polymerase Plasma membrane contain lipid with ester bound Most bacteria in this kingdom Come in 3 basic shapes --- cocci (spheres), bacilli (rod shaped), spirilla (corkscrew shape) THE STRUCTURE 12 Structure of bacteria Cell Wall protects the cell and gives shape Outer Membrane protects the cell against some antibiotics (only present in Gram negative cells) Cell Membrane regulates movement of materials into and out of the cell; contains enzymes important to cellular respiration Cytoplasm contains DNA, ribosomes, and organic compounds required to carry out life processes Chromosome carries genetic information inherited from past generations Plasmid contains some genes obtain through genetic recombination Capsule, and slime layer protects the cell and assist in attaching the cell to other surfaces Pilus (Pili) assist the cell in attaching to other surfaces, which is important for genetic recombination STRUCTURE FUNCTION the cell Flagellum Mesosom moves the cell To form of cell membrane when cleavage begin To help the sparatition chromosome duplicasted Endospore protects the cell against harsh environmental conditions, such as heat or drought Pili help cells attach to surfaces Pili Figure 16.12B Endospores allow certain bacteria to survive environmental extremes in a resting stage Endospore Figure 16.12C variety of shapes Spheres (cocci) are the most common Rods (bacilli) • Curves or spirals Figure 16.9A-C Kokus (Coccus) dalah bakteri yang berbentuk bulat seperti bola, dan mempunyai beberapa variasi sebagai berikut: Mikrococcus, jika kecil dan tunggal Diplococcus, jka bergandanya dua-dua Tetracoccus, jika bergandengan empat dan membentuk bujursangkar Sarcina, jika bergerombol membentuk kubus Staphylococcus, jika bergerombol Streptococcus, jika bergandengan membentuk rantai Basil (Bacillus) adalah kelompok bakteri yang berbentuk batang atau silinder, dan mempunyai variasi sebagai berikut: Diplobacillus, jika bergandengan dua-dua Streptobacillus, jika bergandengan membentuk rantai Spiril (Spirilum) adalah bakteri yang berbentuk lengkung dan mempunyai variasi sebagai berikut: Vibrio, (bentuk koma), jika lengkung kurang dari setengah lingkaran Spiral, jika lengkung lebih dari setengah lingkaran Streptococcus Diplobasil Campylobacter jejuni, curved (vibrio-shaped), rod 23 BASED ON THE MOVEMENT ORGANS MONOTRIC AMFITRIC LOFOTRIC WHEN THE BACTERIA DON’T HAVE FLAGEL IS CALLED ATRIC PERITRIC Berdasarkan kisaran suhu aktivitasnya, bakteri dibagi menjadi 3 golongan: Bakteri psikrofil, yaitu bakteri yang hidup pada daerah suhu antara 0°– 30°C, dengan suhu optimum 15°C. Bakteri mesofil, yaitu bakteri yang hidup di daerah suhu antara 15° – 55°C, dengan suhu optimum 25° – 40°C. Bakteri termofil, yaitu bakteri yang dapat hidup di daerah suhu tinggi antara 40° – 75°C, dengan suhu optimum 50 - 65°C Bacterial Reproduction & Genetic Recombination Most bacteria reproduce asexually by binary fission (chromosome replicates & then the cell divides) Bacteria replicate (double in number) every 20 minutes under ideal conditions Bacteria contain much less DNA than eukaryotes Bacterial plasmids are used in genetic engineering to carry new genes into other organisms Bacteria recombine genetic material in 3 ways transformation, conjugation, transduction Conjugation • Sexual reproductive method • Two bacteria form a conjugation bridge or tube between them • Pili hold the bacteria together • DNA is transferred from one bacteria to the other Transformation Bacteria pick up pieces of DNA from other dead bacterial cells New bacterium is genetically different from original Transduction Staining properties of bacteria by Danish microbiologist, Hans Gram Purple with Crystal Violet & iodine; rinsed with alcohol to decolorize; then restained with Safranin Then bacteria which become violet are called gram positive and remaining colourless bacteria called gram negative. REACTION OF CELL TO STAINING GRAM Materi Pelatihan Guru 32 Materi Pelatihan Guru 33 Compare gram + and gram - Gram-positive bacteria (Gram +) • Thick layer of peptidoglycan (protein- sugar) complex in cell walls & single layer of lipids • Stain purple Gram-negative bacteria (Gram -) • Cell walls have a thin layer of peptidoglycan & an extra layer of lipids on the outside • Stain pink or reddish • Lipid layer prevents the purple stain & antibiotics from entering (antibiotic resistant Methods of Respiration Obligate aerobic bacteria Obligate anaerobes Facultative anaerobes Anaerobes carry on fermentation, while aerobes carry on cellular respiration Methods of Nutrition Saprobes feed on dead organic matter Symbionts make mutually beneficial association with other organisms. Example Rhizobium in root nodules of legume plants Parasites feed on a host cell Photoautotrophs use sunlight for energy, but get carbon from organic compounds (not CO2) to make their own food Chemoautotrophs obtain food by oxidizing inorganic substances like sulfur, instead of using sunlight THE ROLE