* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Final Jeopary 1
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
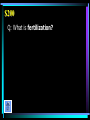
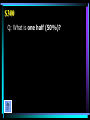
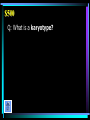
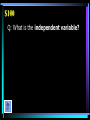
BIOLOGY Edition Warm Up: • Review what quantitative and qualitative observations are. • What is the scientific process? • What is a hypothesis? • What is a theory? • What is a cell and the main parts? Energy Cells Categories Protein Sci Genetics Methods Synthesis Macromolecules $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 Biology $100 A: The process that requires glucose and oxygen. $100 Q: What is aerobic respiration? $200 A: The process that uses carbon dioxide (CO2) and water to make glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen. $200 Q: What is photosynthesis? $300 A: Thylakoids are stacked on top of one another forming grana in this organelle responsible for photosynthesis. $300 Q: What is a chloroplast? $400 A: A chemical process, occurring in the absence of oxygen, that converts glucose to pyruvic acid which is then converted to lactic acid. $400 Q: What is fermentation (anaerobic respiration)? $500 A: The Krebs cycle and electron transport chain take place in the matrix and inner membrane of this organelle. $500 Q: What is the mitochondria? $100 A: A large organelle located near the center of a cell that houses the cell’s DNA. $100 Q: What is the nucleus? $200 A: A type of cell that contains a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. $200 Q: What is a eukaryotic cell? $300 A: The passive transport of water across a membrane. $300 Q: What is osmosis? $400 A: This organelle is the “garbage disposal” of the cell, breaking down old organelles, foreign substances, etc. $400 Q: What is a lysosome? $500 A: These organelles organize the synthesis of proteins; may be “free” in the cytoplasm or bound to the endoplasmic reticulum. $500 Q: What are ribosomes? $100 A: The molecule in a cell responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information (info for making proteins); has the shape of a double-helix. $100 Q: What is DNA? $200 A: The complementary base pairs in DNA. $200 Q: What are guanine-cytosine and adenine-thymine? $300 A: The molecules that are linked together to make a protein. $300 Q: What are amino acids? $400 A: The type of RNA that has an anticodon and brings amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis. $400 Q: What is tRNA? $500 A: The process by which information in DNA is copied to a molecules of mRNA. $500 Q: What is transcription? $100 A: Is represented with a lowercase letter. $100 Q: What is a recessive allele? $200 A: The process in which an egg cell and sperm cell fuse to form a zygote. $200 Q: What is fertilization? $300 A: The fraction of offspring resulting from a Bb x bb cross that should have blond hair. B = brown hair b = blond hair $300 Q: What is one half (50%)? $400 A: The condition in which a person has 2 alleles that are the same for a trait. $400 Q: What what is homozygous? $500 A: A picture of a child’s chromosomes that is used to determine if a child has a genetic disorder, such as Down’s syndrome (extra chromosome #21). $500 Q: What is a karyotype? $100 A: This is the one variable that differs between the control group and experimental group. $100 Q: What is the independent variable? $200 A: Observations that deal with data that can be represented as numbers. $200 A: What are quantitative observations? $300 A: An observation that describes the qualities or characteristics of something. $300 Q: What is a qualitative observation? $400 A: The process that allows humans to use bacteria to produce large quantities of things like insulin and human growth hormone. $400 Q: What is genetic engineering? $500 A: The process that uses restriction enzymes to cut DNA and then separates the fragments by size using gel electrophoresis. $500 Q: What is DNA Fingerprinting? $100 A: An organic molecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; the hydrogen and oxygen are in a 2:1 ratio, like water. $100 Q: What a carbohydrate? $200 A: The monomers (“building blocks”) that make up nucleic acids, DNA and RNA. $200 Q: What are nucleotides? $300 A: An organic compound with a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail; organizes into a bilayer which makes up the cell membrane. $300 Q: What is a lipid? $400 A: The contestant on the right, who is currently losing, will win $400 if she can name the reaction that builds polymers. $400 Q: What is a dehydration synthesis reaction? (a.k.a.: condensation reaction) $500 A: Enzymes, molecules that speed up the rates of chemical reactions, belong to this class of macromolecules. $500 Q: What are proteins?