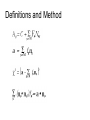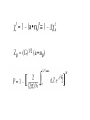* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download reduce
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative comparative linguistics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sequence alignment wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
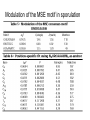
Regulatory element detection using correlation with expression (REDUCE) Literature search WANG Chao Sept 14, 2004 Harmen J. Bussemaker, Hao Li & Eric D. Siggia, Regulatory Element Detection Using Correlation with Expression, Nature Genetics vol 27, 167 (2001) Some points • A new method for discovering cis-regulatory elements • A new method for discovering cis-regulatory elements • A single genome-wide set of expression ratios, The upstream sequence for each gene, Outputs statistically significant motifs. Extract biologically meaningful information ● • One method for discovering them groups genes into disjoint clusters based on similarity in expression profile over a large number of different conditions. • The new method selects the most statisticaly significant motifs from the set of all oligomers up to a sepecified length, dimers(two oligomers with a fixed spacing) and groups thereof based on sequence alignment. Result four aspects of this algorithm: • the iterative selection of motifs to optimize their independence • the construction of weight matrices from groups of significant dimers • following the fitting parameters as a function of time to infer function • analyzing the modulation of a consensus motif by variable positions and flanking bases Definitions and Method Finding motifs relevant to cell cycle Time courses for cell cycle and sporulation motifs Modulation of the MSE motif in sporulation Some points to discussion • reduces experimental noise and is well suited for uncovering groups of genes • a quantitative expression of the widespread notion18 that transcription initiation occurs through the recruitment of the polymerase by reversible binding to transcription factors and hence to the regulatory sequences • reconfirm almost all motifs found by clustering methods, at least to the extent of finding a related sequence motif that captures the same experimental signal • the importance of simultaneously fitting as many genes as possible The end