* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Epistasis is not dominance.
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
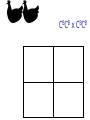
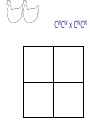
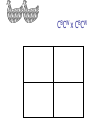
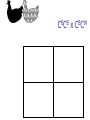
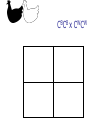
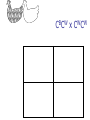
Other Inheritance Patterns Intermediate Inheritance The heterozygote has a phenotype that is intermediate between the phenotypes of the two homozygotes. Example: Petal color in certain flowers. Codominance The heterozygote expresses both traits at the same time. In this example, the heterozygous chickens are speckled. They express both feather colors at the same time. CBCB x CBCB CWCW x CWCW CBCW x CBCW CBCB x CBCW CBCB x CWCW CBCW x CWCW Sex-Linked Inheritance Genes located on sex chromosomes produce different patterns in males and females. Females generally have two alleles for these genes. Males generally have only one allele. If a male inherits a sex-linked recessive allele from his mother, the allele will be expressed. Red/Green Color Blindness Epistasis Effects of one gene override or mask the phenotype of a second gene. Epistasis is not dominance. Compare the definitions: Epistasis: One gene masks the expression of a different gene for a different trait Dominance: One allele masks the expression of another allele of the same gene Example of Epistasis Labrador retrievers can be black, brown, or yellow. Two genes control this. One gene influences melanin production B (black) is dominant to b (brown) One gene influences melanin deposition E (full deposition) is dominant to e (reduced deposition) Polygenic Inheritance Continuous variation Most traits show a range of variation rather than distinct either/or types This occurs when multiple genes and environmental factors influence the trait’s expression Continuous variation is often described with frequency distribution tables. Example using actual data