* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Controls - Warren`s Science Page
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
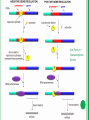
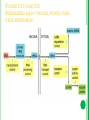
CHAPTER 15.1 When Controls Come Into Play AP Biology Fall 2010 NEW VOCABULARY Promotors: are short stretches of base sequences in DNA where regulatory proteins gather and control transcription of specific genes, often in response to a hormonal signal Enhancers: binding sites where such proteins increase transcription rates Methylation and Acetylation: are the names for the addition of such groups to DNA or any other molecule Cell Differentiation: nearly all of your body cells became specialized in composition, structure, and function GENE EXPRESSION Because all cells in your body have the same genetic instructions…… Only a relatively small number of genes are active at any given time in any given tissue Which genes are expressed depends on the type of cell, its responses to chemical signals, and built-in control systems Regulatory proteins interact with DNA, RNA, or actual gene products SOME CONTROL MECHANISMS In negative control systems, a repressor protein binds to the DNA to block transcription It can be removed by an inducer In this case a response slows or stops some activity SOME CONTROL MECHANISMS In positive control system, an activator protein binds to the DNA and promotes initiation of transcription In this case a response enhances some activity txn factor = transcription factor VOCABULARY Remember: Promoters: short stretches of base sequences in DNA where regulatory proteins control tanscription of specific genes Enhancers: are the binding sites in DNA where regulator proteins are found to be increasing transcription rates Controls can be exerted by chemical modification – methylation and acetylation – of DNA Methyl groups (-CH3) are “painted” on parts of newly replicated DNA to block access to genes Acetyl groups (-CH3CO-) are attached to DNA to make genes accessible POINTS OF CONTROL There are four ways that genes in multicelled organisms are turned off and on to maintain homeostasis POINTS OF CONTROL 1. Controls before transcription: Histone interactions that limit access of RNA polymerase to genes Methylation and Acetylation of DNA functional groups Make histones loosen their grip Polytene chromosome formation Contain hundreds or thousands of side-by-side copies of genes Duplication and rearrangement of DNA sequences Remember: access to a gene is under control! POINTS OF CONTROL 2. Control of transcript processing: Removal of part of the RNA transcript (introns) Modification of RNA (attachment of proteins) So it can pass through the nuclear pores Controls when the mRNA transcript reaches a ribosome Special codes in the mRNA that determine where in the cell’s cytoplasm it will be used Y-box protein that can bind to a transcript to block its translation When phosphorylated Y-box proteins bind and help stabilize mRNA When many of the proteins bind to a transcript, they block its translation Control mechanism in mRNA inactivation INTRONS AND EXONS (PG. 232 MUSCLE CELL EXAMPLE) POINTS OF CONTROL 3. Controls of translation: Interactions of ribosomal subunits and initiation factors and the stability of mRNA transcripts before degradation begins POINTS OF CONTROL 4. Controls after translation: Addition of phosphate to the Y-box proteins Activates Y-box Other controls activate, inhibit, and stabilize diverse molecules that take part in protein synthesis Allosteric control of enzymes in metabolic pathways REMEMBER ALLOSTERIC? SAME GENES, DIFFERENT CELL LINEAGES All body cells have the same genes, but the cells of different tissues are differentiated (specialized) because of selective gene expression Every body cell arose by mitotic division from the same fertilized eggs Nearly all of your body cells become specialized in composition, structure, and function (Cell Differentiation) For example: Red blood cells transcribe genes for hemoglobin Genes in the eye make crystallin for the transparent lens FIGURE 15.3 PAGE 233 SUMMARIZES MAIN CONTROL POINTS OVER GENE EXPRESSION