* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Engineering
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
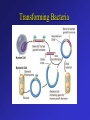
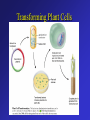
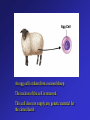
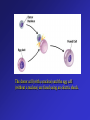
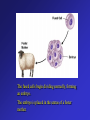
Frontiers of Biotechnology Changing the Living World • These dogs are all of the same species • Where do their striking differences in appearance come from? Beef Cattle Breeds Selective Breeding • A method of improving a species by allowing only those individual organisms with desired characteristics to produce the next generation – Nearly all domestic animals and crop plants have been produced by selective breeding Luther Burbank • American botanist 1849 – 1926 • Developed more than 800 varieties of plants in his lifetime – Developed disease resistant potato to help fight Irish potato blight Hybridization • Breeding technique that involves crossing dissimilar individuals to bring together the best traits of both organisms Inbreeding • The continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics – Breeds developed through inbreeding are genetically similar – Increased chances of bringing together two recessive alleles for genetic defects Increasing Variation • Breeders can increase genetic variation in a population by – Inducing mutations • Mutations are the ultimate source of genetic variability Variation – New Kinds of Bacteria • Mutation rates increased by using radiation or chemicals – Increases the chances of producing a useful mutant • Hundreds of useful bacterial strains have been produced Variation – New Kinds of Plants • Polyploid plants – Plants with double or triple the normal number of chromosomes – Produced by using drugs that prevent chromosomes from separating during meiosis Manipulating DNA Tools of Molecular Biology • DNA extraction – DNA can be extracted from cells by simple chemical procedures • Cutting DNA – DNA can be cut into smaller fragments by the use of restriction enzymes • Separating DNA – Gel electrophoresis – procedure used to produce DNA “fingerprints” Cell Transformation • During transformation, a cell takes in DNA from outside the cell – External DNA becomes a part of the cell’s DNA Transforming Bacteria Transforming Plant Cells Transforming Animal Cells • Can be transformed in some of the same ways as plant cells • Has applications in gene replacement therapy Applications of Genetic Engineering • Transgenic organisms – Transgenic organisms contain genes from other organisms • Transgenic microorganisms • Transgenic animals • Transgenic plants Cloning • Clone • A member of a population of genetically identical cells produced from a single cell Cloning Dolly A donor cell is taken from a sheep’s udder. The nucleus of this cell will provide the genetic material for the cloned lamb. An egg cell is taken from a second sheep. The nucleus of the cell is removed. This cell does not supply any genetic material for the cloned lamb. The donor cell (with a nucleus) and the egg cell (without a nucleus) are fused using an electric shock. The fused cells begin dividing normally, forming an embryo. The embryo is placed in the uterus of a foster mother. The embryo develops into a lamb, Dolly. Dolly is a clone of the sheep that donated the udder cell. A cross between dissimilar individuals to bring together their best characteristics is called a. genetic engineering b. inbreeding c. hybridization d. sequencing Crossing individuals with similar characteristics so that those characteristics will appear in the offspring is called a. inbreeding b. electrophoresis c. hybridization d. genetic engineering Varieties of purebred dogs are maintained by a. selective breeding b. hybridization c. inbreeding d. genetic engineering Changing the DNA of an organism is called a. genetic engineering b. hybridization c. selective breeding d. inbreeding