* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacterial Genome Structure, Replication and Gene regulation
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
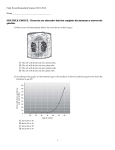
Genomics and other “omics” • Genome sequencing - individual organism (genomics), community of organisms (metagenomics) • Searching the databases • Transcriptional analysis (transcriptomics) • Proteomics • Metabolomics (detect small metabolites) 1 Genomic analysis: Step 1. Predicting open reading frames (orfs) by computer algorithms 2 Genomic analysis: Step 1 (cont.). Predicting open reading frames by computer algorithms • Advantages – Gives a readout of large open reading frames • Limitations – Some genes have start codons that are not ATG – Ignores very small open reading frames. May miss hormone-like peptides, small regulatory peptides, quorum sensing peptides. – Does not detect small regulatory RNAs. 3 Genomic analysis: Step 2. Database searches • DNA sequence alignments – Best for finding nearly identical genes – Find sequence motifs (e.g., helix-turn-helix in DNA binding proteins) • Linear amino acid sequence alignments – Best for finding homologs that may be more distantly related – Annotation can be ambiguous • Example: Elongation factors and tetracycline resistance genes (ribosomal protection type) • Example: Enzymes that are not present in an organism • Annotations are hypotheses!!! • Structural predictions – structural homologs 4 BLASTP 2.2.6 [Apr-09-2003] SusA-8-03 Query= (565 letters) Database: Completed Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482; 1,480,858 sequences; 476,119,222 total letters Distribution of 26 Blast Hits on the Query Sequence Sequences producing significant alignments: gi|29349112|ref|NP_812615.1| gi|29349106|ref|NP_812609.1| gi|29350098|ref|NP_813601.1| gi|29347073|ref|NP_810576.1| gi|29350097|ref|NP_813600.1| gi|29346181|ref|NP_809684.1| gi|29346183|ref|NP_809686.1| gi|29346689|ref|NP_810192.1| gi|29347520|ref|NP_811023.1| gi|29345677|ref|NP_809180.1| gi|29346515|ref|NP_810018.1| gi|29347070|ref|NP_810573.1| gi|29348342|ref|NP_811845.1| gi|29349419|ref|NP_812922.1| gi|29348421|ref|NP_811924.1| gi|29346850|ref|NP_810353.1| gi|29345906|ref|NP_809409.1| gi|29347285|ref|NP_810788.1| Score E (bits) Value alpha-amylase (neopullulanase)... alpha-amylase, susG [Bacteroid... alpha-amylase precursor [Bacte... pullulanase precursor [Bactero... pullulanase precursor [Bactero... 1,4-alpha-glucan branching enz... alpha-amylase 3 [Bacteroides t... putative anti-sigma factor [Ba... hypothetical protein [Bacteroi... two-component system sensor hi... phosphoglycerate mutase 1 [Bac... phosphoglycerate mutase [Bacte... Methionyl-tRNA synthetase [Bac... DNA-methyltransferase [Bactero... putative outer membrane protei... putative outer membrane protei... TonB-dependent receptor [Bacte... putative outer membrane protei... 1076 79 67 61 59 45 38 35 33 30 29 29 28 28 28 28 27 27 0.0 1e-15 6e-12 2e-10 2e-09 1e-05 0.002 0.019 0.094 0.47 1.0 1.0 2.3 2.3 2.3 3.0 4.0 5.2 5 Protein Structure Prediction 6 “Transcriptomics” – Measuring gene expression directly (mRNA) • Types of analysis – Microarray – measures expression of many genes at a time – RT-PCR – measures expression of one gene at a time • Advantages – Microarrays, like transposon mutagenesis, find previously unsuspected genes of interest – Not necessary to make fusions to every gene • Disadvantages (compared to fusions) – Microarray data needs to be checked by RT-PCR – Fusions can be made to monitor translation 7 Microarray - Measuring Gene Expression of Many Genes at a Time 8 New variations of the microarray approach • Make a few labeled DNA copies of each mRNA using RT-PCR – increases sensitivity • DNA copies of mRNA from cells grown under different conditions labeled with different fluorophores (e.g. red for low iron, green for high iron), then mixture is placed on a single slide 9 10 Uses of microarrays • Compare gene expression under different conditions • Determine effects of mutations, eg, in regulatory proteins – effect may be more complex than you thought! • Effects of overexpression of certain genes – less commonly done 11 Metagenomics – genome sequencing of entire bacterial populations • Sample contains bacterial population (e.g. water sample, human colon contents) • Total DNA extracted, non-DNA impurities removed • High throughput sequencing (e.g. 454 sequencing) • Limitations – Assembly – Interpretation!! • Transcriptome – RT-PCR amplifies messages as DNA, sequence DNA – Limitation: lots of rRNA, random priming of RT-PCR 12 Proteomics • Detects proteins produced under different conditions • Two dimensional gel creates an array of protein spots – First dimension: isoelectric focusing (pH gradient) – Second dimension: SDS denaturing gel • Proteins extracted individually, fragmented by proteases, run through a mass spectrometer – matched with fragments predicted from DNA sequence. • Advantages – Detect proteins not RNA (post transcsriptional regulation • Limitations – – – – Only the most highly expressed proteins are detected Overlapping spots may be difficult to resolve Need to go through the MS step Not likely to be useful in metagenomics 13 Conclusions (according to AAS) • Availability of new technologies is forcing a shift from single gene-single pathway thinking to a more global way of thinking. • Increased need to focus on a specific biological question • Most technologies now provided by centralized services – technology itself is uninteresting, only interesting thing is what you can do with it!! 14