* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Yeobeyondgenome_final
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Cooperative binding wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
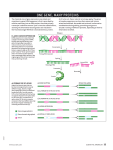
Intronic Splicing Regulatory Elements Genome-wide comparative genomics Array-based discovery from neural differentiation of human ES cells C. Carson J. Simon Eric Van Nostrand, Tiffany Liang Gene Yeo, Salk Institute Nicole Coufal, Christian Carson, Alysson Muotri, Xiangdong Xu, Tiffany Liang, Rusty Gage Understand the rules to predict (cell-type, signal-induced specific) alternative splicing Constitutive Constitutive Alternative Constitutive Constitutive ACEScan[+] exons on UCSC browser Yeo, PNAS 05 NMDA receptor 1 Sorek, Sugnet, Yeo Cell-type specific AS controlled by ciselements and trans-factors UAGG GGGGG UC-rich; UCUU UGCAUG Identification Of Intronic Splicing Regulatory Elements 161,730 exons 24.2 Mb exonic sequence 129 Mb intronic sequence 1. Count conserved kmers and unconserved kmers 2. Derived a chi-square score for significantly enriched and conserved kmers 3. Clustered the kmers into motif families 156 upstream motif clusters 158 downstream motif clusters Example of a downstream motif cluster: TGCATG ,TGCATGA, ATGCATG, CTGCATG, TGCATGC, TGCATGT, TGCATGG, GTGCATG What are the properties of these motifs? •Positional biases? •Near alternatively spliced exons? •Expression biases? •Overlap known elements? I. ISREs have strong positional distribution biases 76% of downstream ISREs exhibit significant position biases 80% of upstream ISREs exhibit significant position biases New protocol for computing conserved positional bias, while controlling for background conservation II. ISREs are enriched near alternative exons 30% downstream ISREs 56% upstream ISREs Some resemble known binding sites FOX1,2 Enriched near muscle alternative exons (Ares) Nova1,2 MBNL CELF PTB III. Genes containing ISRE-proximal exons are tissue-specific Expression biases (71% downstream ISREs, 81% upstream ISREs) IV. ISREs overlap with Exonic Splicing Silencers ESE Fairbrother WG, Yeh RF, Sharp PA, Burge CB (2002) ESS Wang Z, Rolish ME, Yeo G, Tung V, Mawson M et al. (2004) ISE Yeo G, Hoon S, Venkatesh B, Burge CB (2004) ESE, ESS Zhang XH, Chasin LA (2004) Like ESS, do ISREs affect Splice Site Choice ? Competing 5’ss and 3’ss reporter (Wang et al, Mol Cell, July, 2006) Downstream ISREs suppress intron-proximal 5’ splice sites Upstream ISREs suppress intron-proximal 3’ splice sites Applications of ISREs: (1) splicing arrays --tissue specific alternative splicing? included muscle skipped included skipped brain Enriched ISREs in downstream introns QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. TGCATG ACTAAC TTGGTT TGGTTT GCATG TCATTTT TTTCAT Enriched Depleted Sugnet et al. PLoS Comput Biol, 2006 Applications of ISREs: (2) predicting RNA binding sites 1. Several proteins have been reported to affect their own alternative splicing (e.g. hnRNP A1, SRP20, SC35, TIA1, TIAR2, FOX2, PTB) 2. Evolutionarily conserved AS exons have high intronic conservation flanking the exon, resulting in algorithms that perform genomic predictions of alternative conserved exons 3. Alternative conserved exons are enriched in genes encoding RNA binding proteins and splicing factors Applications of ISREs: (2) predicting RNA binding sites Applications of ISREs: (2) predicting RNA binding sites ISREs are likely functional • ISREs identified in mammals via comparative genomics. • ISREs have positional biases, are enriched in tissue-specific genes, and overlap with ESS. • ISREs alter splice site choice in vitro. • Some ISREs resemble known sites of known alt splicing factors. • A fraction of ISREs are proximal to alternative exons. • ISREs can be utilized to analyze splicing-array data. • ISREs can be utilized to identify autoregulated exons, and has other implications. Alternative splicing differences in human embryonic stem cells versus neuronal progenitors hESC NP from hESC 1. Developed an algorithm to detect AS from exon arrays (REAP). 2. Verify AS events. 3. Identify ISREs proximal to AS events. 4. Identify RNA binding protein. Endogeneous NP Exon arrays have probesets in every exon Simple representation Exon array, alternative splicing, gene expression Tiling arrays REAP predictions agree with A) EST-verified alternative splicing B) ACEScan[+] exons Confirming isoforms by RT-PCR Discovery of ISREs proximal to ES/NP alternative exons ISREs in ES/NP ongoing… • REAP algorithm designed for exon array based detection of AS events • REAP[+] exons correlate with EST-based and ACEScan[+] exons • ISREs identified specific for ES/NP AS events • FOX1/2 may regulate ES/NP-specific AS events Alternative splicing at the Crick-Jacobs Center, Salk Institute Computational Modeling, Integration Constitutive Alternative Constitutive Stem cells, early neuronal differentiation Cis-elements Association of RNA binding proteins to elements QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture.