* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Counseling
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
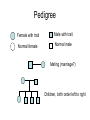
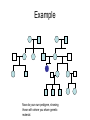
Genetic Counseling Making a Pedigree By Diana L. Duckworth Rustburg High School Campbell County Pedigree Female with trait Male with trait Normal female Normal male Mating (marriage?) Children, birth order left to right Example Now do your own pedigree, showing those with whom you share genetic material. Sex Linked Gene • The y chromosome has very few genes • Any gene on the X chromosome is sex linked • If the phenotype is found predominantly in males, then it is sex linked • If recessive, female must be homozygous to express the gene • Any male possessing the allele will have the phenotype • Example: albinism & hemophelia Genetic Disease • Sickle Cell Anemia – abnormal hemoglobin molecules; 1/500 African Americans; recessive • Hypercholesterolemia – abnormal receptor for cholesterol; dominant; 1/500 • Tay-Sachs – defective brain enzyme; recessive; 1/3500 in Ashkenazi Jews (children) • Cystic Fibrosis – recessive; defective chloride ion transport protein; 1/2500 Caucasians • Hemophilia – sex-linked recessive; blood clotting factor defective; 1/10000 • Huntington’s Disease – inhibitor of brain cell metabolism; (middle age); dominant; 1/10,000