* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download You Light Up My Life
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
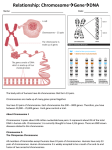
Environment-induced disruptions in meiosis BPA treated Chromosome number error (aneuploidy) rose from 1-2% to 40% in mouse eggs! Reason- bisphenol A (BPA), a component of plastic.. ….. results in meiosis errors in mouse eggs Meiosis normal Science 300:31 April 2003 Chromosomes and Human Genetics Chapter 11 Chromosomes and Cancer Genes on chromosomes drive ___________ __________ is uncontrolled cell division Philadelphia Chromosome •First abnormal chromosome to be associated with a cancer •Associated with a chronic ________ •Overproduction of white blood cells •Due to _____________________ Genes • Units of information about _______________ • Each has a particular __________ – Location on a _______________ •_______________ are identical in length, size, shape, and gene sequence Alleles A B C A B C a b c a b c •Different __________ forms of a gene •Arise through _____________ _______________- display of chromosomes Fig. 11.4, p. 173 Blood sample 1000X magnification 1 2 3 4 13 14 15 16 5 17 6 7 8 9 18 19 20 21 10 22 11 12 XX (or XY) Sex Chromosomes • Discovered in late ______ • Mammals, fruit flies – XX is _______, XY is _________ • In other groups XX is male, XY female eggs sperm X Sex determination Y X X Female germ cell Male germ cell X X X XX XX Y XY XY sex chromosome combinations possible in new individual The Y Chromosome • < ____ genes • Includes ____ gene- dictates ______ phenotype The X Chromosome • > ______ genes • Most genes - _______ traits • Genes expressed in both males and females Effect of Y Chromosome appearance of structures that will give rise to external genitalia appearance of “uncommitted” duct system of embryo at 7 weeks 7 weeks Y present Y absent Y present Y absent testes ovaries 10 weeks ovary birth approaching testis • Thomas Hunt Morgan - first to associate a specific gene with a specific chromosome in the early 20th century. • Morgan’s model-Drosophila melanogaster, a fruit fly - have three pairs of __________ and a pair of _____________ chromosomes (XX in females, XY in males). Red eyes White eyes Normal is called “_________” Non-normal is called “______” Know these symbols = _ _____ _ • Morgan’s experiments- = _______ _ Red eye X White eye F1 All Red eye 3:1 Red:white F2 Conclude- classic _ ________ _ genetics But- all __________were white, all females red Morgan concluded that a fly’s eye color was linked to the _ _____________ ___. Fig. 15.3 Linked genes tend to be inherited together because they are located on the same chromosome 15.3 15.2 15.1 14 13.2 13.3 13.1 12 11 11.1 11.2 12 Chromosome- 1.5 x 108 base pairs containing about ______ genes 13.1 13.2 13.3 14 15 21 22 23.1 23.2 23.3 31.1 31.2 31.3 32 33.2 33.1 33.3 34 35.2 35.1 35.3 0.4% of a chromosome, containing 10 genes • Genes located on the same chromosome,___ ______ _______, tend to be inherited together because the chromosome is passed along as a unit. •Results of crosses with linked genes deviate from those expected according to __ _____________________ __. Linkage Groups • Genes on one type of chromosome • Fruit flies – __ homologous chromosomes – __ linkage groups Crossover Frequency -____________to the distance that separates genes A B C D Crossing over will disrupt linkage between _________ more often than _________ Frequencies can be used to construct a _______________ Incomplete Linkage AC A C Parents: ac c x A a a c C F1 offspring All AaCc meiosis, gamete formation Unequal ratios of four types of gametes: C A c a Most gametes have parental genotypes c A a C A smaller number have recombinant genotypes Linkage Mapping in Humans Called a “________” • Chart that shows _____________ connections among individuals • Knowledge of probability and Mendelian patterns used to suggest basis of a trait Pedigree for __________ Unusual number of toes or fingers Genetic Disorders •_________ conditions that cause mild to severe medical problems Autosomal _________ •Many people are _________ •Heterozygous parents-child will have a _____ chance of being affected Autosomal __________ •Trait typically appears in _______ generation •Most of these ________ from population. WHY? Autosomal dominant diseases 1. Huntington Disorder • Causes involuntary movements, nervous system deterioration, death • Symptoms don’t usually show up until person is past age ___ • People often pass allele on before they know they have it 2. Acondroplasia •In homozygous form usually leads to _______ • Heterozygotes display a type of _________ • Have short arms and legs relative to other body parts X-Linked Recessive Inheritance • Males show disorder _________ females • Son _______ inherit disorder from his father Examples 1. Color blindness2. _________, Blood-clotting disorder; 1/7,000 males 3. ________- Allele has repeated segments of DNA; causes mental retardation 4. ____________________ - Appears to be dominant; spontaneous mutation; premature aging effect, early death The wrong number of chromosomes is bad Usually due to ________________ n+1 n+1 n-1 chromosome alignments at metaphase I n-1 nondisjunction at anaphase I alignments at metaphase II anaphase II • Nondisjunction results in too many or to few chromosomes termed ______________ . – some gametes receive two of the same type of chromosome and another gamete receives no copy. – _______ cells - three copies of a particular chromosome type and have _______ total chromosomes. – _________ cells - one copy of a particular chromosome type and have 2n - 1 chromosomes. • Normally results in embryonic death, but some survive Organisms with more than two _______ _sets of chromosomes, have undergone _________, e.g. 3n or 4n (rare in ____________) • Polyploids are more nearly normal in phenotype than ___________. Other chromosome problems A ________- a chromosome fragment lacking a ________ is lost during cell division A ___________- a fragment becomes attached as an extra segment to a sister chromatid Fig. 15.13c & d • An inversion - a chromosomal fragment ________ to the original chromosome but in the reverse orientation. • In_ _______, a chromosomal fragment joins a _________ chromosome. •Some translocations are ___________ others are not. Results of chromosome errors • Homozygous embryos with a large ________ normally die • A deletion in the X chromosome is _______ in males • A __ ________________ can alter phenotype because a gene’s expression is influenced by its location. Example- Leukemia is due to a growth gene being placed next to an active region resulting in cancer • Approx. _____ of human embryos are aneuploid and die early in development Some are viable• Chromosome 15 trisomy- die at birth • Chromsome 21 trisomy- ________ syndrome • Down syndrome- trisomy 21. – One in 700 children born in the United States. – result from ___________________ during gamete production • correlates with the age of the mother. Fig. 15.14 Karyotype Phenotype Extra sex chromosomes are allowed • _____________________ _an XXY male, occurs once in every 2000 live births. – Male sex organs, but are_ ________. – Feminine characteristics; normal intelligence. • Males with an extra Y chromosome (XYY) tend to somewhat _______ than average. • Trisomy X (XXX), which occurs once in every 2000 live births, produces _ ________ _ females. • Monosomy X or _____________ (X0), which occurs once in every 5000 births, produces phenotypic, but immature females. • XYY and XXYY- males often found in _________. • In utero testing for genetic screening. 1. _____________ - beginning at the 14th to 16th week of pregnancy to assess the presence of a specific disease. Fig. 14.17a •Fetal cells extracted from amniotic fluid are cultured and __________. • 2. _____________ ________(CVS)- performed as early as the eighth to tenth week of pregnancy. – Extracts a sample of fetal tissue from the chrionic villi of the placenta are karyotyped. Fig. 14.17b • Other techniques____________________________ allow fetal health to be assessed visually in utero. – usually reserved for cases in which the risk of a genetic disorder or other type of birth defect is relatively great. • If fetal tests reveal a serious disorder, the parents face the difficult choice of terminating the pregnancy or preparing to care for a child with a genetic disorder.