* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics - Fort Bend ISD
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
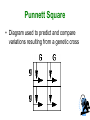
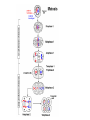
Introduction to Genetics Ch. 11 Write the information on the slides that show this symbol or that is this color. Genetics • The scientific study of heredity Gregor Mendel • Father of modern genetics • Combined plant breeding, statistics, careful record keeping Mendel studied pea plants traits (characteristics) Genetic Information • Gene – basic unit of genetic information Allele – one form of a gene Principle of Dominance • Some alleles are dominant and others are recessive Dominant vs. Recessive •Dominant alleles express a trait. (capital letter) •Recessive alleles are only visible when paired with another recessive allele. (lower case letter) Segregation Separation of alleles during gamete formation Gamete Sex cells Punnett Square • Diagram used to predict and compare variations resulting from a genetic cross Homozygous vs. Heterozygous • Homozygous - having two dominant or two recessive alleles. (BB or bb) •Heterozygous - having both a dominant and recessive allele. (Bb) Genotypes Phenotypes • Genotype - genetic make up • Phenotype – physical characteristics Genotypes Phenotypes (example) genotypes phenotypes Hybrid • Offspring of crosses between parents with different traits Principle of Independent Assortment • Genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes. • Example: genes for seed shape segregate independently of those for seed color Incomplete Dominance • One allele is not completely dominant over another Incomplete Dominance • A flower has genes for white petals (w) and red petals (r). When you mix white flowers with red flowers you get pink flowers. How is this possible? The w gene does not dominate over the r gene and vice versa. Both genes express themselves equally so you get a pink color in the petals. w w r wr wr r wr wr Codominance • Both alleles contribute to the phenotype Polygenetic Traits • Traits controlled by two or more genes Meiosis • reproduction of gametes (Similar to mitosis, but there are 2 divisions, ending with ½ the number of chromosomes of the parent cell.) Diploid vs. Haploid • Diploid – contains both sets of homologous chromosomes • Haploid – contains a single set of chromosomes Crossing-over is the process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis. Gene Map • Diagram showing the relative locations of each known gene on a particular chromosome