* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics PowerPoint
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
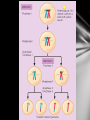
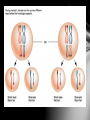
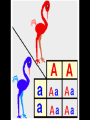
Genetics The study of heredity Mendel 1860’s Austrian Monk Worked with pea plants Used his math background to make new hypotheses about inheritance. Mendel’s Experiments Example of Mendel’s work Mendel hypothesized that each trait is controlled by a “factor” 2 or more “factors” for each trait •Dominant-more powerful, always shows (R) •Recessive-weaker, sometimes shows (r) Mendel knew that 2 parents contribute to inheritance. Therefore, each organism must have 2 factors for each trait. These factors later became known as genes. Purebred (homozygous) •both genes the same •RR, rr Hybrid (heterozygous) •genes are different •Rr Mendel’s 3 Laws 1. Law of Segregation – genes separate when gametes form 2. Law of Dominance – when 2 different alleles in a gene pair are present only one gene is expressed Law of Independent Assortment – gene pairs segregate into gametes randomly and independent of each other. 3. Genotype – the actual genetic makeup of the organism Phenotype – the form of the trait expressed (letters) (word) Punnett Square Used to predict the outcome of a genetic cross. Dihybrid Cross: 2 factors 1. Assign letters 2. Set up cross 3. Create Punnett square 4. Determine genotypes 5. Determine phenotypes Golden fur is dominant over silver fur. Long fur is dominant over short fur. 1. Cross a homozygous golden long furred dog with a heterozygous golden furred dog with short hair. Golden fur is dominant over silver fur. Long fur is dominant over short fur. 2. Cross a homozygous silver long furred dog with a heterozygous golden long furred dog.