* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics Test
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human–animal hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome-wide association study wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
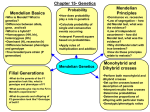
Genetics Test Study Guide Resources: 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, and 7.2 from the textbook, all notes from class (including genetics, incomplete dominance, codominance, and dihybrid crosses). Key Questions: 1. What name has been given to Gregor Mendel and what are his key contributions to the field of genetics? 2. List the three laws developed by Gregor Mendel. 3. What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? Give an example of each. 4. What is the difference between a homozygous and heterozygous genotype? Give examples of each (use R and r). 5. What do the terms hybrid and purebred mean? 6. What plant did Mendel do the majority of his research on? 7. Explain the difference between a dominant trait and a recessive trait? 8. Define the following terms: Gene, allele, trait, heredity. 9. What is the difference between genome and a genotype? 10. What is the value of a Punnett square? 11. Explain the difference between a monohybrid cross and a dihybrid cross. 12. Which of Mendel’s laws is illustrated in a dihybrid cross? 13. What is the law of segregation? 14. What is the law of dominance and does it apply to all genetic traits? 15. Explain the difference between a codominant trait and an incomplete dominance trait. Give examples to explain. 16. What phenotype ratio did Mendel discover in a dihybrid cross with all heterozygotes? 17. What is a multiple allele trait? Give an example. 18. What are P, F1, and F2 generations? Problems: 1) Be able to solve and identify problems in dominance, incomplete dominance, codominance (including ABO bloodtyping), and dihybrid crosses. 2) Be able to identify and put together genotypes and phenotypes with given information. Practice Problems 1) In humans, hitchikers thumb (H) is dominant to a normal thumb (h). a. What is the hybrid genotype? b. If two heterozygous individuals are crossed, what is the phenotype ratio that will result? 2) In cattle, RR is red, WW is white and RW is roan (red and white splotches). What type of inheritance is displayed? 3) Refer to question number 2. Two roan cattle are crossed. a. What is the expected genotype ratio? b. What percentage are expected to be roan? 4) A man is heterozygous for blood type A. His wife is heterozygous for blood type B. a. What is the chance that their first child will have blood type O? b. If their first child ends up with type AB blood, what is the chance that their second child will end up with type AB blood? 5) In sasquatch, red fur (R) is dominant to brown fur (r) and wirey fur (F) is dominant to silky fur (f). Methusaleh has hybrid red, silky smooth fur and Gretchen has brown, hybrid wirey fur. a. What are Methusaleh’s and Gretchen’s genotypes (Be sure to label. You must get both right for credit.) b. What is the chance that they will have a child that is genetically identical (concerning the two traits involved) to Methusaleh? 6) Refer to question 5. If two sasquatch are crossed with the following genotypes: RrFf X RrFf, what will be the resulting phenotype ratio?