* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Methods of asexual reproduction
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
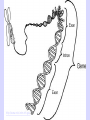
Methods of Reproduction Types of Reproduction • There are two main ways in which reproduction occurs: – Asexual Reproduction – Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction: requires only 1 parent and the offspring are an exact copy of the parent---a clone Asexual Reproduction: • Organisms that reproduce asexually cannot develop much variety, because they are “copying” the original organism exactly. Methods of asexual reproduction: Binary fission Budding Fragmentation Binary fission Single-celled organisms (Amoeba, paramecium, euglena) which use asexual reproduction can do so simply by dividing into two equal halves. This is called binary fission. • When conditions are good, such as plenty of water, food, right temperatures, etc., binary fission is a very effective way of producing many, many offspring. • For example, the cell of a Paramecium can divide, grow, and divide again in the space of 8 hours. Budding- an offspring grows out of the body of the parent. offspring Hydra Budding Cactus Budding Budding In yeasts the cell does not divide equally in two halves; instead, there is a large mother cell and a smaller daughter cell. Yeast - budding Fragmentation In this form, the body of the parent breaks into distinct pieces, each of which can produce an offspring. Pieces of coral broken off in storms can grow into new colonies. A new starfish can grow from one detached arm. Fragmentation- plant cuttings Some plants can grow from cutting them up and replanting them. Green plants are quite sophisticated in their methods of asexual reproduction. Offspring may be produced by runners, bulbs, rhizomes or tubers. What is sexual reproduction? • Requiring 2 parents – male and female • Offspring are different from the parent organism because it takes half the DNA from one parent and half from the other Sexual Reproduction • Sexual reproduction produces a greater chance of variation within a species than asexual reproduction would. • This variation improves the chances that a species will adapt to his environment and survive. Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction • Asexual reproduction results in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent organism. • Sexual reproduction results in offspring that are genetically different from the parent organisms. DNA – Chromosomes Genes DNA •DNA: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms. •The scientific name for DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ Chromosomes A chromosome is one of the threadlike "packages" of genes and other DNA in the nucleus of a cell. Different kinds of organisms have different numbers of chromosomes. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, 46 in all. Each parent contributes one chromosome to each pair, so children get half of their chromosomes from their mothers and half from their fathers. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov Gene • A gene is the functional and physical unit of heredity passed from parent to offspring. • Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain the information for making a specific protein. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov Genome • A genome is all the DNA contained in an organism or a cell, which includes the chromosomes plus the DNA in mitochondria (and DNA in the chloroplasts of plant cells). http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov Cell division and DNA replication • Cells divide • Growth, Repair, Replacement • Before cells divide, they have to double cell structures, organelles and their genetic information DNA replication – Mitosis & Meiosis Videos • Asexual Reproduction/Binary Fission – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DY9DNW cqxI4 • Budding in Yeast: – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iOvrq6ssy2 Y • Regeneration: – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EsCSwVx3 GvA