* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is so memorable about CREBBP?
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
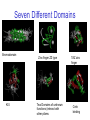
What is so memorable about CREBBP? (RSTS; RTS, CBP CBP/MOZ FUSION GENE, CREB-binding protein) Where is it found? What exactly does “BP” mean • Binding protien • What is a coactivator and what is its role? • Does it perform one function (interaction) or does it perform many? pg224 of book • http://www.ebi.ac.uk/intact/search/do/search?searchString=EBI81215&filter=ac&searchClass=Protein&view=partner&filter=ac What is its function and where is it found? Gene Ontology Ontology Molecular Function Gene Ontologies Biological Process Cellular Component Annotation Evidence Source Histone acetyltransferase activity IEA GOA/IPI Signal transducer activity Transcription coactivator activity Transcription coactivator activity Protein binding Transcription factor activity Transferase activity Zinc ion binding Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent Regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent Response to hypoxia Homeostasis Signal transduction Protein complex assembly Cytoplasm Nucleus Nucleus TAS IEA IPI IPI TAS IEA IEA IEA TAS TAS NAS NAS TAS TAS IEA TAS GOA/IPI GOA/IPI GOA/IPI GOA/IPI GOA/IPI GOA/IPI GOA/IPI GOA/IPI GOA/IPI GOA/IPI GOA/IPI GOA/IPI GOA/IPI GOA/IPI GOA/IPI GOA/IPI Normalized Expression (%) Cluster Clones : Tissue clones posterior tongue (pooled): 22.02 2:473 Brain: 10.61 1:491 liposarcoma: 5.31 1:980 lymph: 3.84 15:20369 Trabecular meshwork: 3.65 2:2854 metastatic prostate bone lesion: 3.24 2:3214 fibrotheoma: 2.51 3:6234 prostata: salivary gland: myeloid cells, 18 pooled CML cases, BCR/ABL rearrangement positive, includes both chronic phase and myeloid blast crisis: 2.21 2.07 1:2355 1:2521 Tissue Normalized expression distribution for tissue type Top ten 2.01 1:2589 What makes up the coding sequence? It is made of 32 exons and 31 introns. The mRNA itself is 8.7 kb, 7.3 of that is coding! Enough about its genome, lets talk protein! • • The protein is made of 2442 amino acids and is 265 kDa! That’s nice, but what does it look like? Seven Different Domains Bromodomain KIX Zinc finger ZZ type Two Domains of unknown functions (interact with other pfams TAZ zinc finger Creb binding So now that I know what its made of and where its found…. What does it do? • Mediates cAMP-gene regulation by binding specifically to phosphorylated CREB protein. CREBBP, as coactivator, augments the activity of phosphorylated CREB to activate transcription of cAMPresponsive genes. • What do we know about cAMP and memory? pg.223 Sounds nice, but what does that have to do with memory? • • • • • http://www.dnai.org/text/mediashowcase/index2.html?id=483 CREB turns on other genes to store in long term memory. Switched on to create new connections between nerve cells Turning off and on genes by the act of remembering. In other words, CREB is a gene that mediates long-term memory. It acts as a master gene that turns on other genes, assisted by CREBBP • Evidence for this function- studies on CREBBP transgenic mice suggests that competition for CBP plays an important role in regulating gene expression during cell growth. CREBBP and p300 function as transcriptional coactivators in the regulation of gene expression through various signal transduction pathways Diseases associated with CREBBP • Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome • Result of germline mutation of CREBBP • myeloid leukemias • MLL translocations involving the CREBBP gene have primarily been reported in treatment-related acute myeloid lukemia after chemotherapy for other primary malignancies using topoisomerase II inhibitors. References Ridley, Matt. "Chromosome 16, Memory." Genome, The Autobiography of a species in 23 Chapters. New York: Harper Perennial, 1999. 219-230. http://www.dsi.univ-paris5.fr/genatlas/fiche.php?symbol=CREBBP (slide 2,6) http://atlasgeneticsoncology.org/Genes/CBPID42.html (slide 10) http://genome-www5.stanford.edu/cgibin/source/sourceResult?criteria=CREBBP&choice=Gene&option=Symbol&organism=Hs (slide 4, 8) http://www.ihop-net.org/UniPub/iHOP/gismo/87420.html (slide and 9) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/guide/human/ (slide 1) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=gene&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=full_report&list_uid s=1387 (slide 5) http://www.ebi.ac.uk/intact/search/do/search?searchString=EBI81215&filter=ac&searchClass=Protein&view=partner&filter=ac (slide 3) http://www.sanger.ac.uk/cgi-bin/Pfam/qquerypfam.pl?terms=crebbp (slide 7)