* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LECTURE OUTLINE Cell Structure & Function DNA Replication
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
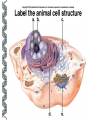
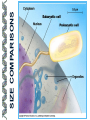
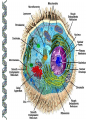
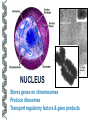
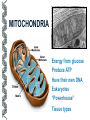
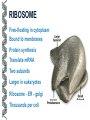
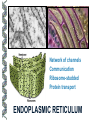
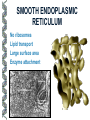
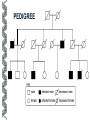
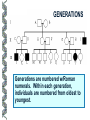
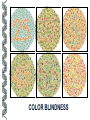
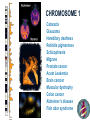
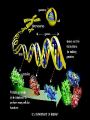
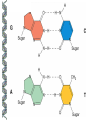
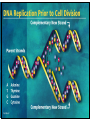
LECTURE OUTLINE Cell Structure & Function DNA Replication Protein Synthesis Mutations Simple Inheritance Genetic Disorders SIZE COMPARISONS MUTATIONS PHOSPHOLIPID MEMBRANE Compartmentalization Protection Cell recognition Entry/exit Fluid mosaic NUCLEUS Stores genes on chromosomes Produce ribosomes Transport regulatory factors & gene products MITOCHONDRIA Energy from glucose Produce ATP Have their own DNA Eukaryotes “Powerhouse” Tissue types RIBOSOME Free-floating in cytoplasm Bound to membranes Protein synthesis Translate mRNA Two subunits Larger in eukaryotes Ribosome - ER - golgi Thousands per cell GREGOR MENDEL Network of channels Communication Ribosome-studded Protein transport ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM No ribosomes Lipid transport Large surface area Enzyme attachment GOLGI APPARATUS Polar ends Flattened sacs Vesicles ER Packaging center Proteins Cells w/secretory role CENTRIOLE Right angle cylinders Microtubules Spindle fibers Cell division Tongue Roll Attached Earlobe Tongue Flip Unattached Earlobe Tongue Fold Hitchhiker’s Thumb Ear Diagram Ear Wax Bent Pinky Hand Fold Dimples Mid-digital hair PTC Tasting Bent Little Finger Widow’s Peak Short Hallux Finger Length Autosomal Recessive Traits Only expressed in individuals that have two copies of the relevant gene. More frequent with inbreeding, isolated groups. Autosomal Dominant Traits Expressed even if only one copy of the gene is inherited. Effects sometimes show up later in life. Sex-linked Traits Associated with genes on the X chromosome. Chromosomal Abnormalities Deletions, Duplications, Inversions, Translocations Nondisjunction and Aneuploidy Extra or missing chromosomes female marriage proband consanguineous marriage diseased male Dizygotic twins Affected individuals Extra-marital mating progeny carrier ? Unknown phenotype identical Female carrier of an x-linked trait Stillborn or abortion (monozygotic) twins PEDIGREE GENERATIONS Generations are numbered w/Roman numerals. Within each generation, individuals are numbered from oldest to youngest. AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT INHERITANCE Approximately a 1:1 ratio of affected vs. unaffected progeny with one affected parent. Transmission can occur from affected father to affected son. Direct transmission from an affected parent to an affected child. (Affected children always have an affected parent.) AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE INHERITANCE Affected parents can have affected offspring. However, affected children typically do not have affected parents. Affected individuals can be either male or female. More affected males than females. Affected grandfather to grandson thru carrier female. SEX-LINKED RECESSIVE TRAITS Females do not manifest the disorder. Examples of sex-linked recessive traits: COLOR BLINDNESS Examples of sex-linked recessive traits: COLOR BLINDNESS DOMINANT DISEASE Huntington’s Disease • Woody Guthrie • Arlo Guthrie • Children Lobster Foot Dominant allele -- you have the disease or you don’t RECESSIVE DISEASE • Albinism • Achondroplasia • Both parents can be carriers to have an affected child • 2 affected parents will usually produce an affected • Dominant doesn’t necessarily meanchild commonplace AVERY, MACLEOD, MCCARTY 1944 -- First experimental evidence that DNA transmits genetic information. FRANKLIN, WATSON, CRICK, WILKINS 1953 -- Using an x-ray pattern of DNA generated by Rosalind Franklin, Maurice Wilkins, James Watson and Francis Crick publish their double-helix model DNA. 1962 -- Wilkins, Watson & Crick win Nobel Prize NIRENBERG & KHORANA 1960-1966 -- protein synthesis described They decipher the genetic code that all living cells use to translate the series of bases in their DNA into instructions for the production of proteins. SMITH, NATHANS & ARBER 1970 -- Hamilton Smith discovers the first restriction enzyme that cuts DNA at specific sites. Daniel Nathans & Werner Arber use restriction enzymes to generate the first physical map of a chromosome. BERG, GILBERT, MAXAM & SANGER 1977 -- working separately, each develop techniques for rapidly ‘spelling out” long sections of DNA by determining the sequence of bases. Chimp Orangutan Gorilla 48 48 48 Gibbons Siamang 44 50 Colobus Green Monkey Baboon Owl Monkey Squirrel Monkey 44 60 42 54 44 Ringtailed Lemur Black Lemur 56 44 CHROMOSOME 1 Cataracts Glaucoma Hereditary deafness Retinitis pigmentosa Schizophrenia Migrane Prostate cancer Acute Leukemia Brain camcer Muscular dystrophy Colon cancer Alzheimer’s disease Fish odor syndrome CHROMOSOME 2 Colon cancer Obesity Liver cancer Diabetes mellitus Cleft palate Cataracts Epilepsy Parkinson’s disease Muscular dystrophy Pseudohermaphroditism Ovarian cancer Micropenis CHROMOSOME 4 Huntington’s disease Night blindness Phenylketonuria Parkinson’s disease Alcoholism Red hair Mast cell leukemia Achondroplasia Dopamine receptor Retinitis pigmentosa Hip dysplasia XO 1/2500 live births