* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9/18 Recombination and chromosome mapping
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
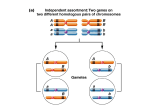
Chapter 7 Outline • 7.1 Linked Genes Do Not Assort Independently, 161 • 7.2 Linked Genes Segregate Together, and Crossing Over Produces Recombination between Them, 162 • 7.3 A Three-Point Testcross Can Be Used to Map Three Linked Genes, 175 • 7.4 Physical Mapping Methods Are Used to Determine the Physical Positions of Genes on Particular Chromosomes, 185 • 7.5 Recombination Rates Exhibit Extensive Variation, 188 7.1 Linked Genes Do Not Assort Independently 7.2 Linked Genes Segregate Together and Crossing Over Produces Recombination between Them 7.2 Linked Genes Segregate Together and Crossing Over Produces Recombination between Them • Notation for Crosses with Linkage • Complete Linkage Leads to Nonrecombinant Gametes and Nonrecombinant Progeny • Crossing Over with Linked Genes Lead to Recombiant Gametes and Recombinant Progeny Calculating Recombination Frequency • Recombination frequency = (number of recombinant progeny / total number of progeny) × 100% Coupling and Repulsion Configuration of Linked Genes • Coupling (cis configuration): Wild type alleles are found on one chromosome; mutant alleles are found on the other chromosome. Coupling and Repulsion Configuration of Linked Genes • Repulsion (trans configuration): Wild-type allele and mutant allele are found on the same chromosome. Testing for Independent Assortment Concept Check 2 The following testcross produces the progeny shown: AaBb × aabb 10 AaBb, 40 aaBb, 40 aaBb, and 10 aabb. What is the percentage of recombination between the A and B loci? Were the genes in the AaBb parent in coupling or repulsion? Concept Check 2 The following testcross produces the progeny shown: AaBb × aabb 10 AaBb, 40 aaBb, 40 aaBb, and 10 aabb. What is the percent recombination between the A and B loci? Were the genes in the AaBb parent in coupling or repulsion? % recombination: 20%; genes in the AaBb parent were in repulsion Gene Mapping with Recombination Frequencies • Genetic maps are determined by recombinant frequency. • Map unit and centiMorgans Constructing a Genetic Map with TwoPoint Testcrosses 7.3 A Three-Point Testcross Can Be Used to Map Three Linked Genes • Constructing a Genetic Map with the Three-Point Testcross Constructing a Genetic Map with the Three-Point Testcross • Determining the gene order • Determining the location of crossovers Concept Check 3 Write the genotypes of all recombinant and nonrecombinant progeny expected from the following three-point cross: Concept Check 3 Write the genotypes of all recombinant and nonrecombinant progeny expected from the following three-point cross: Answer: Concept Check 4 A three-point test cross is carried out between three linked genes. The resulting nonrecombinant progeny are s+r+c+ and s r c, and the doublecrossover progeny are s r c+ and s+r+c. Which is the middle locus? Concept Check 4 A three-point test cross is carried out between three linked genes. The resulting nonrecombinant progeny are s+r+c+ and s r c, and the doublecrossover progeny are s r c+ and s+r+c. Which is the middle locus? the C locus • Calculating the recombination frequencies • Interference and coefficient of coincidence • Effect of multiple crossovers • Mapping human genes 7.4 Physical Mapping Methods Are Used to Determine the Physical Positions of Genes on Particular Chromosomes • Deletion Mapping • Somatic – Cell Hybridization