* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics - VA Biology SOL
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
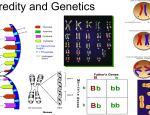
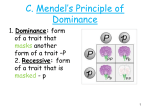
CATALYST Catalyst: Complete a dihybrid cross for a Heterozygous Tall person and a Homozygous Short Person. T = Tall, t = Short Mr. Gibney will start this on board promptly when bell rings CURRENT EVENT BY FRIDAY!!!! HOMEWORK REVIEW CURRENT EVENTS (I will give you till Wednesday) -HELP US See Science in everyday life “Very nice résumé. Leave a sample of your DNA with my secretary.” Gibney Bucks Review!!! How do mitosis and meiosis differ? How are people either male or female? What is DNA? What is replication? What is transcription? What is translation? When is Reading day this week? STUDY ROCK THIS CLASS YOU CAN BRING YOUR GRADE UP IF YOU TRY! Think for a second about the most crazy thing you have ever seen… Imagine in the future… when something like THIS could be possible… The future is now… WELCOME TO GENETICS!!! Follow Along • In Book Ch 10 • Fill in guided notes as we go along and if you miss something… check out the book! •WHY THIS IS IMPORTANT!!!!!! GENETICS the study of how traits are passed from one generation to the next TRAIT a characteristic Examples: Plant size, seed color, pod shape TRAITS YOU MIGHT HAVE… Can you curl your tongue? Can you wiggle your ears? Can you raise just one eyebrow? USA: 82% Yes USA: 27% Yes USA: 64% Yes GENES Each feature of the pea plants is controlled by a gene. It may have a gene that controls its color, another for size and another for shape. GENE the factors that control traits (found in the DNA) Above you see chromosomes. The circled area is a gene on chromosome #22. The absence of this gene causes velo-cardiofacial syndrome (VCFS) which may cause ADD and mental illness ALLELES Each gene comes in different forms called alleles, so the gene that controls flower color may come in two alleles: purple and white. ALLELES different forms of a gene PURPLE MAN EATER PLANT EXAMPLE Traits: 6ft tall, purple, eats people Genes that control these traits are on Chromosome 17 Each of the three genes has different alleles: Can be 6ft tall or 3 ft tall, purple or orange, eat people or vegetarian GREGOR MENDEL The “father” of genetics Lived from 1822-1884 Austrian Monk Published his work in 1866, but no one took him seriously until 1900. Studied Pea Plants! MENDEL’S EXPERIMENTS Mendel experimented with 7 different characteristics Mendel Got Lucky for 2 Big Reasons 1. 2. First, he had a lot of time…he was a monk. This let him do LOTS of experiments with the peas! Each trait had 2 options. This was key because he could tell if it was one way or the other. VOCABULARY • "Think! How the hell are you gonna think and hit at the same time?" HOMOZYGOUS organism with two identical alleles for the same trait (TT or tt) HETEROZYGOUS organism with two different alleles for the same trait (Tt) DOMINANT allele that is expressed when in the presence of a recessive allele (TT or Tt = tall) RECESSIVE allele that is expressed only when homozygous (tt = short) PHENOTYPE physical characteristics (Tall, Brown) GENOTYPE the genetic makeup (TT, TtHh) GENE = Height ALLELE = Tall, Short Gene is represented by the letter “t” Dominant = T Recessive = t Remember you need 2 copies of every gene!!! How can we determine what the offspring are going to be? PUNNETT SQUARES Reginald C. Punnett • Inventor of the Punnett Square PUNNETT SQUARES chart showing the possible combination of alleles in a cross Punnett Squares show the probability of getting a certain type of offspring THE PARENTS GENOTYPES • DAD = Tt (heterozygous) • MOM = Tt (heterozygous) PHENOTYPES • DAD = Tall • MOM = Tall PUNNETT SQUARES THE OFFSPRING GENOTYPES 1TT:2Tt:1tt (1:2:1) • TT (homozygous dominant) • Tt (heterozygous) • Tt (heterozygous) • tt (homozygous recessive) THE OFFSPRING PHENOTYPES 3 Tall :1 Short (3:1) • TT (tall) • Tt (tall) • Tt (tall) • tt (short) STUDENT DEMOS UP FRONT • Do student demonstration with genotypes • Do bag demonstration with beans tomorrow Cross a homozygous dominant with a recessive (for height where T is dominant and tall). Find the genotype and the phenotype Cross a heterozygote with a recessive (for height where T is dominant and tall). Find the genotype and the phenotype Cross a heterozygote with another heterozygote (for skin color where Black is B, b = white). Find the genotype and the phenotype Cross a heterozygote with another heterozygote (for nose size where big nose is N and small nose is n). Find the genotype and the phenotype • When you flip a quarter, what are the odds that a coin turns up heads? What about when you flip two coins at the same time, what are the odds that both turns up heads? • Coin Flip Lab • Coin 1 Coin 2 HeadsTailsHeadsTails % Heads% Tails% Heads% Tails Test Cross A cross between an unknown and a homozygous recessive Example of a Test Cross Unknown Codominance When a combination of the dominant and recessive creates a new phenotype. RR = red, rr = white, and Rr = pink Codominance RR Rr rr Codominance Cross Codominance Cross Sex Linked Trait a trait that is found on either the X or Y chromosome Hemophilia is an example of a sex linked trait. Hemophilia a disease where your blood doesn’t clot. Hemophilia only occurs when all of the X chromosomes have a copy of the recessive gene. H h X X :female carrier h h X X :female hemophiliac H X Y:normal male h X Y:hemophiliac male SICKLE CELL ANEMIA Difference between normal cells & sickle cells Sickle Cell SS = normal Ss = carrier (SC trait) ss = sickle cells (lethal) Sickle Cells tend to get stuck easily in the circulatory system. Why would African American’s be so much more likely to have Sickle Cell? Regular red blood cells infected by malaria PEDIGREE chart that shows the relationships within a family Pedigree Basics • Males are squares, females are circles, and unborn babies are triangles or octagons • Shaded figures represent individuals with the trait, a carrier could be 1/2 shaded • Generations are numbered with roman numerals (I, II, II, IV) from top to bottom • People within generations are numbered (1,2,3) from left to right PEDIGREE HELP!!!! 200 B.C. Humans “clone” trees by cuttings 1950 Humans clone frogs 1980’s Humans clone mice! 1997 HUMANS CLONE SHEEP!!! 1998 Humans clone 8 copies of a cow!!! 20?? GENETIC ENGINEERING moving genes from one chromosome of one organism to the chromosome of another “Fat” Gene CLONING making an exact copy of another cell / organism Dolly—the first cloned sheep Ian Wilmut, the dude that did it Check out this short movie that talks about cloning… A dividing cell Read NYTimes Article "Despite Warnings, 3 Vow to Go Ahead on Human Cloning" a. What did three proponents of human cloning announce on August 7, 2001? b. Where did they make this announcement? c. Why did some scientists at the symposium object to the proponents' announcement? d. Why did Dr. Alan Colman object to the research by these proponents being done in secret? e. According to the article, what was the consensus among the panel and most of those who testified before it? Read NYTimes Article "Despite Warnings, 3 Vow to Go Ahead on Human Cloning" f. Who was "Dolly"? g. What animals have been successfully cloned? h. According to the article, what is involved in cloning a human? i. How did the three proponents say they would address the possibility of genetic abnormalities? j. How did other experts at the symposium respond to this statement? k. Why do the proponents need to conduct their research secretly? •http://www.biology.arizona.edu/human_bio/activities/karyot yping/karyotyping.html •http://www.pathology.washington.edu/galleries/Cytogaller y/cytogallery.html •http://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourses/N100/2k2humancs omaldisorders.html •http://www.biology.washington.edu/bsa/karyotypeS.html •http://worms.zoology.wisc.edu/zooweb/Phelps/karyotype.html AMNIOCENTESIS A technique used to determine the genetic traits of a baby before it is born Klinefelter Syndrome • Have male genitalia and internal ducts, but underdeveloped testes • Do not produce sperm • Slight enlargement of the breasts • 47,XXY • 1 out of every 500 male births Turner Syndrome • • • • • • • Has female external genitalia Underdeveloped ovaries Short (under 5 feed) Webbed Neck Broad, Shield-like chest 45,X 1 out of every 3000 female births Cri-du-Chat Syndrome • Partial monosomy (part of 1 chromosome is lost) • Loss of about 1/3 of the short arm of chromosome 5 • Anatomical malfomrations (gastrointestinal and cardiac complications) • Mentally retarded • Abnormal development of the larynx which makes the baby’s cry sound like a cat’s cry • 1 in 50,000 live births Down Syndrome • • • • • • • • • BKA trisomy 21 (47, 21+); 3 copies of the 21st chromosome Short Small round heads Protruding, furrowed tongues which cause mouth to remain partially open Retarded (IQ below 70) Shortened life expectancy (<50) Prone to reparatory disease and heart malformations Have 15x higher chance of getting leukemia Chance of having a baby with Down syndrome goes up as the mother gets older Guided Notes Mini-Clinical: 10pts I meant to start these backup again but got caught up in the excitement of getting a room. On a clean sheet of paper answer the following… you may use your notes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. How do the base pairs in DNA matchup? What is the difference between DNA and RNA? How do transcription and translation differ? Name 2 scientists that we talked about who helped “discover” DNA Draw the pathway from DNA to protein. TRADE N GRADE How do the base pairs in DNA matchup? A-T, G-C Pedigree Basics • Males are squares, females are circles, and unborn babies are triangles or octagons • Shaded figures represent individuals with the trait, a carrier could be 1/2 shaded • Generations are numbered with roman numerals (I, II, II, IV) from top to bottom • People within generations are numbered (1,2,3) from left to right