* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
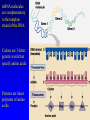
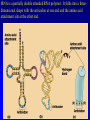
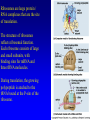
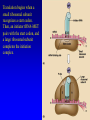
Gene Expression II: Translation and Mutations 5 November, 2004 Text Chapter 17 mRNA molecules are complementary to the template strand of the DNA. Codons are 3-letter genetic words that specify amino acids. Proteins are linear polymers of amino acids. In translation, mRNA sequence specifies protein sequence with the help of tRNA adapter molecules. In the genetic code, 5’ UUU 3’ specifies Phenylalanine, so the anticodon is 3’AAA 5’. 5’GGC 3’ specifies Glycine, so the anticodon is ‘3 CCG 5’. tRNA molecules are transcribed from DNA templates (genes) and extensively modified. tRNA is a partially double stranded RNA polymer. It folds into a threedimensional shape with the anticodon at one end and the amino acid attachment site at the other end. Amino acids are loaded onto tRNA molecules by AminoacyltRNA synthetase. In the cell there is a different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase for each of the twenty amino acids. Ribosomes are large protein / RNA complexes that are the site of translation. The structure of ribosomes reflects ribosomal function. Each ribosome consists of large and small subunits, with binding sites for mRNA and three tRNA molecules. During translation, the growing polypeptide is atached to the tRNA bound at the P-site of the ribosome. Translation begins when a small ribosomal subunit recognizes a start codon. Then, an initiator tRNA-MET pairs with the start codon, and a large ribosomal subunit completes the initiation complex. Elongation Cycle Termination of translation occurs when release factor binds to a stop codon in the A-site. Then, the completed protein, the mRNA, and the ribosomal subunits are released. Each mRNA may be translated thousands of times. tRNA molecules can be re-used after recharging, and ribosomal subunits are recycled for use translating another mRNA. Proteins destined to be exported or transported inside the cell contain signal sequences that direct the protein into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. Then, the protein folds into its final threedimensional shape. Mutations are changes in DNA sequence. These changes can lead to altered proteins. The altered proteins are usually non-functional. Types of Mutations The Ames test identifies mutagenic chemicals by their ability to cause reversion in a Salmonella histidine auxotroph that carries a single-base missense mutation.