* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Problems in Replication and Protein Synthesis
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
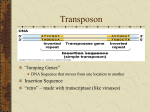
Gene Mutations and Expression Mutations -mutation- random change in genetic material -can happen during replication, transcription, translation, or cell division Point Mutations -Point mutation – a single base pair is affected -It could be a deletion, insertion, or substitution. Substitution Insertion • Extra base pair is added (causes a frameshift) Deletion • Base pair is removed (causes frameshift) Duplications -duplication- part of the DNA is duplicated Inversions -inversion - part of the DNA is reversed A-T-C-G-T-T-G-C A-T-C-G-T-C-G-T Translocations -part of the DNA is moved to a different spot A-A-A-T-C-G-T-A-C T-C-G-A-A-A-T-A-C Mutation Outcomes Missense – the wrong amino acid is added Mutation Outcomes • Nonsense – a stop codon is produced early causing the amino acid chain to end early. Mutation Outcomes • Silent – although the wrong codon is produced but the correct amino acid is sill added (thus no change) • Wobble – more than one codon can code for the same amino acid. (makes silent mutations possible) Prokaryotic Gene Regulation • Operator – a control site within the promoter that can be blocked to stop transcription (turns the gene off) • Repressor – a protein that slides into the operator to block transcription (the RNA polymerase cannot attach and pass) • Operon – promoter + operator + genes they control Co-repressor • Co-repressor – a molecule that combines with the repressor to change the repressor into its active form. (thus turning the gene off) • Ex. E. Coli in our colon only make the amino acid Tryptophan if we are not providing it for them. Negative regulation • Negative regulation – gene is off until turned on • Repressor is naturally active • Ex. If no lactose (from milk) is present in the colon E. Coli does not produce enzymes to break down milk Inducer (negative) • Inducer – molecule that bonds with the repressor to make it inactive (turns the gene on) • If milk is present E. Coli turns on genes to produce enzymes to break down the milk. Positive Gene Control • Positive regulation – even though the repressor is inactive and the gene is on, protein production must be stimulated. • Ex. If lactose and glucose are both present E. Coli chooses to use glucose and does not produce enzyme to break down lactose (even though the lactose operon is on) Activator Activator (positive) • Activator – stimulates the production of a protein in a gene that is on (calls for RNA polymerase to attach) • If glucose is in short supply and lactose is available, E. Coli. will produce enzymes to breakdown lactose. Activator Eukaryotic Regulation • Enhancers – sites that call for specific activators to stimulate the production of certain proteins. Histone Acetylation • Histone Acetylation – acetyl groups are added to histone tails (neutralizes their charges) • Histones spread exposing DNA so transcription can be initiated. DNA Methylation • DNA methylation – a methy group is added to a base. (usually found in inactive genes) Proteasomes • Proteasomes - degrade old protein • Ubiquitin – molecules added to proteins needed to be broken down. Micro and Small Interfering RNA • Micro RNA (miRNA) – single stranded degrades or blocks translation of mRNA. • Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) - double stranded but functions similarly to siRNA (may help fight viruses)