* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrients
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
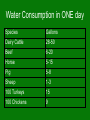
Nutrients Nutrients Topic 3040 Topic Ashlee3040 Gibson Ashlee Gibson http://www.hinztechnologies.com/Images/hay.jpg Objectives • To identify the different parts of a feed ration • To understand how nutrient aids in animal growth and development What is a nutrient? • A substance that is necessary for an organism to live and grow • Nutritional requirements depend on: – Age – Stage of development – Environmental conditions – Activity – Genetic make-up What is the most important nutrient? • Water • Function – Temperature regulation – Chemical reactions – Transport – Gives body form Water Consumption in ONE day Species Gallons Dairy Cattle 28-50 Beef 6-20 Horse 5-15 Pig 5-8 Sheep 1-3 100 Turkeys 15 100 Chickens 9 Carbohydrates • Compound composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Examples include starches and sugars. – Energy from the breaking of bonds • They form about 75% of all dry matter in plants. • They are the CHIEF SOURCE OF ENERGY in animal feed. Types of Carbohydrates • Starches – Grain, root crops, other plant materials • Sugars – Simple sugars (monosaccharides) – Double sugars (disaccharides) – Milk and fruit • Fiber – Plant cell walls and cellulose – Fermented by bacteria in foregut of ruminant and hind gut fermentors (require in their diet) Lipids (Fats) • Aids in the absorption of vitamin A (and other fat soluble vitamins) from food and especially of carotene. • Helps in the absorption of calcium. • Increases the palatability of a ration. • Increases the production energy of the ration. • Is found as a component in every cell in the body. • 2.25 times more energy than carbohydrates More energy in fats so why not feed more fat than carbohydrates? • Not enough protein uptake – Young animals will not reach maximum growth • Destroy certain fat soluble vitamins. • Produce soft lard in hogs. Protein Protein needed for – Cell construction – Muscle formation and maintenance – Fetal Growth – Extra protein is broken down for body energy Made Up of Amino Acids Protein is EXPENSIVE Amino Acids Amino acid requirements of animals depends on: – The kind of animal. – Body functions of the animal: • • • • age work lactation fetal growth Protein When feeding protein • The amount of protein. • The quality of protein. • The compliment of amino acids in proteins www.asasoya.org/Images/collage4.jpg Ruminants vs Non-Runinants Protein Ruminants can make essential amino acids • Done by rumen bacteria • from simple forms of nitrogen Urea • Only used for Ruminants • Protein substitute – Source of nitrogen of rumen organisms to produce bacteria • Used only in small amounts http://agnews.tamu.edu/dailynews/stories/ANSC/photos/Mar0206a-lr.jpg Protein • Location of Protein in feed material • The "germ" is the part of the grain kernel which usually contains available protein. www.angelfire.com/folk/molinologist/whkernel.gif Vitamins • Vitamins job in the body: – regulate body functions – keep body healthy – develop resistance to disease • Do not provide body with energy Vitamins • Fat Soluble- stored in fat – A,D,E,K • Vitamin K is produced in animal’s intestinal tract • Vitamin D is produced from the sun • Water Soluble- dissolved by water – Need to be consumed everyday – B,C Minerals • Macrominerals – Need in large amounts – Calcium- causes bones and teeth to form properly – Phosphorus- key ingredient in the body’s use of protein – Iron- makes hemoglobin in red blood cells – Iodine– Magnesium- lack causes muscle tremors and shakes – Sodium and potassium- water balance, transfer nutrients and waste through the cell membrane • Microminerals – Need in small amounts