* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download presentation source
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Alpha helix wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
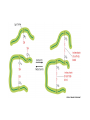
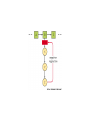
Week 3 Inter-chain interactions • Quanternary structure of proteins – interaction between 2 or more polypeptides – Disulfide bridges • cysteine -S-S- cysteine • --CH2-S-S-CH2-• see Fig. 5-22 Disulfide bridges • Bridge between two cysteines • catalyzed by endoplasmic reticulum enzymes • broken by reducing agents, e.g., mercaptoethanol and dithiothreitol – CH2-S - S-CH2 - ------> -CH2 -SH + HS-CH2- Enzymes • • • • • Catalytic proteins not permenantly changed during catalysis need native structure to be active do not alter Keq or delta Go lower activation energy of reaction – see Figures 3-12 and 3-14 Factors affecting enzymes • Temperature – increases thermal motion of atoms – disrupts hydrogen bonds • pH – change protonation patterns of amino acids which affects ionic bonds • Ion concentration – interferes with ionic bonds between amino acids Enyzme-substrate interactions • Enzyme like a “glove” and substrate like a “ball” – substrate fits in the active site of the enzyme like a ball fits in the glove. – See Figure 5-24 and 5-27 • E+S ---> ES -->EP --> E + P – E-enzyme; S-substrate; P-product Parameters of enzymes • See Figure 5-30 • V is the velocity of the enzyme • Vmax is the maximum velocity of enzyme – can be in the order of 1000’s substrate molecules per second! • Km is a measure of the affinity of an enzyme for its substrate – lower the Km the greater the affinity – Km= substrate concentration at 1/2 Vmax Michaelis-Menten Equation • V=Vmax [S/(S+Km)] • Transform above equation = LineweaverBurk plot – 1/V = (Km/Vmax) x (1/S) + (1/Vmax) – equation for a straight line • where 1/Vmax= y intercept • and (1/S) = x-intercept – X-intercept = -1/Km Enzyme regulation • Allosteric proteins – proteins with second binding site for “affector molecules” • protein changes conformation when affector molecule binds to the allosteric site • see Figure 5-34 • Feedback inhibition - negative feedback – see Figure 5-32 • Feedback stimulation - positive feedback Enzyme regulation • Phosphorylated vs dephosphorylated state – kinase adds phosphate group – phosphatase removes phosphate group – See Figure 5-36 • GTP-binding – See Figure 5-38 Enzyme cofactors • Co-enzymes – NAD+, FAD • Prosthetic groups – heme, biotin, retinal • metallic cations – Zn++, Mg++, Fe++, Fe+++, Cu++, Na+, and K+ Protein analysis • Refer to Panels 5-4, 5-5 & 5-6 of your text Enyzme nomenclature