* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzymes
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Mitogen-activated protein kinase wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Ultrasensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
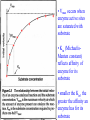
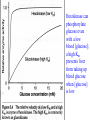
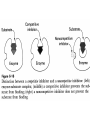
Enzymes • Large molecules made of various amino acids • Act as catalysts to speed up reactions w/out being destroyed – Highly specific – Lowers energy of activation level Enzymes lower the energy of activation for a reaction Enzyme Kinetics E + S ES complex E + P • Effect of substrate concentration – 10 test tubes of fixed [E] – Add gradations of [S] – Measure rate of reactions • Vmax occurs when enzyme active sites are saturated with substrate • Km (MichaelisMenten constant) reflects affinity of enzyme for its substrate • smaller the Km, the greater the affinity an enzyme has for its substrate Enzyme Kinetics • [S] generally < than its Km – Only uses fraction of enzyme catalytic ability – Enzyme is able to respond to changes in [S] • Isozymes (isoenzymes) are variations of same enzyme – Four isozymes of hexokinase • Three have low Km and fourth has a high Km Hexokinase can phosphorylate glucose even with a low blood [glucose]; a high Km prevents liver from taking up blood glucose when [glucose] is low Regulation of Enzymes • Enzymes concentration – Will increase Vmax but not Km – Vmax proportional to [E] • Competitive inhibition Regulation of Enzyme Kinetics • Competitive inhibition – – – – have similar geometric shape Compete with enzyme for substrate Can be overcome by [S] Will not affect Vmax but will Km Regulation of Enzyme Kinetics • Allosteric regulation (noncompetive inhibitor/stimulator) – Allosteric enzymes don’t follow MichaelisMenton kinetics; rather, most follow a sigmoidal model – Does not bind to active site on E • Changes shape of E which either of ability to bind with S – Will change Vmax but not Km Regulation of Enzyme Kinetics • Phosphorylation – cAMP activates protein kinase – activates catabolic enzymes – inactivates anabolic (synthetic) enzymes • Effect of temperature, pH Metabolic Pathway E1 E2 E3 A ------> B ------> C ------> D initial substrate final substrate First step is usually irreversible and controlled by an allosteric enzyme