* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reviewing Enzymes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
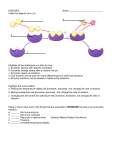
Reviewing Enzymes • - All enzymes are proteins...proteins are also called “polypeptides”. • - Enzymes are made up of amino acids (amino group + carboxyl group (an organic acid) + “R” group”) • - held together by “peptide bonds” (bond between C and N) • - most enzymes end with “ase” • - Enzymes are “Biochemical catalysts”..... they trigger or accelerate a chemical reaction without being chemically altered themselves. • Enzymes are very “specific”. • Enzymes lower the amount of activation energy required to start a reaction. An Enzyme Reaction includes an enzyme, a substrate, and products. • A Substrate is the molecule(s) acted upon in an enzyme reaction. • The Product(s) of a reaction are “What you make” as a result of a chemical reaction. Coenzymes • Organic molecules that aid in enzyme reactions. • Many Vitamins are Coenzymes. The distinguishing feature of the vitamins is that they generally cannot be made by mammalian cells and, therefore, must be supplied in the diet. Cofactors • Non-protein molecules, or ions, which aid in enzyme reactions. • Examples: Zinc, Iron and Copper.