Platelet surface glutathione reductase-like activity
... cause disruption of the ␣IIb3 receptor (5 mM EDTA [ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid], 60 minutes, 37°C). Equal amounts of protein were added to lanes 1, 2, and 3. (D) Densitometry of the individual bands was used to obtain quantitative results. The first 2 columns show the ratio of labeling of the  ...
... cause disruption of the ␣IIb3 receptor (5 mM EDTA [ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid], 60 minutes, 37°C). Equal amounts of protein were added to lanes 1, 2, and 3. (D) Densitometry of the individual bands was used to obtain quantitative results. The first 2 columns show the ratio of labeling of the  ...
Thiosulfoxide (Sulfane) Sulfur: New Chemistry and New Regulatory
... completely lacking in the enzyme methylthioadenosine nucleoside phosphorylase (MTAP) [25] and deficient in CTH [17,26]. In direct comparison, cells containing MTAP are not dependent on the sulfur factor [25]. Subsequent to the report of the absence of MTAP in mouse cells, the enzyme was found to be ...
... completely lacking in the enzyme methylthioadenosine nucleoside phosphorylase (MTAP) [25] and deficient in CTH [17,26]. In direct comparison, cells containing MTAP are not dependent on the sulfur factor [25]. Subsequent to the report of the absence of MTAP in mouse cells, the enzyme was found to be ...
Methods to Design and Synthesize Antibody
... leaves normal cells unaffected. More important, many of the cytotoxic drugs that are too toxic for use in traditional chemotherapy can also be used in the construction of antibody-drug conjugates [3,4]. The linkers are also essential parts of antibody-drug conjugates, which account for stability in ...
... leaves normal cells unaffected. More important, many of the cytotoxic drugs that are too toxic for use in traditional chemotherapy can also be used in the construction of antibody-drug conjugates [3,4]. The linkers are also essential parts of antibody-drug conjugates, which account for stability in ...
Protein Structure Hierarchy
... primarily on the protein surface and accordingly, contain polar and charged residues. Antibody recognition, phosphorylation, glycosylation, hydroxylation, and intron/exon splicing are found frequently at, or adjacent to turns. However it is not clear if this is due to specific recognition or simply ...
... primarily on the protein surface and accordingly, contain polar and charged residues. Antibody recognition, phosphorylation, glycosylation, hydroxylation, and intron/exon splicing are found frequently at, or adjacent to turns. However it is not clear if this is due to specific recognition or simply ...
Title The Cyanide-Ion Cleavage of Organic Disulfides
... A. J. Parker, "Advances in Organic Chemistry Methods and Results," Vol. 5, ed. by R. A. Raphael, E. C. Taylor, and H. Wynberg, Interscience Publishers, New York, N. V., 1965, p. 1. ...
... A. J. Parker, "Advances in Organic Chemistry Methods and Results," Vol. 5, ed. by R. A. Raphael, E. C. Taylor, and H. Wynberg, Interscience Publishers, New York, N. V., 1965, p. 1. ...
Intermolecular bonding - Teacher instructions - Lesson element
... paves the way to an understanding of instantaneous dipole–induced dipole bonding and how this is present in all molecules, the strength increasing with the Mr. The relative strengths of the three types of intermolecular bond can be seen from the graph. This activity also offers an opportunity to rev ...
... paves the way to an understanding of instantaneous dipole–induced dipole bonding and how this is present in all molecules, the strength increasing with the Mr. The relative strengths of the three types of intermolecular bond can be seen from the graph. This activity also offers an opportunity to rev ...
Molecular dynamics of serpins
... Conclusion: formation of disulfide bonds between the cysteines in RCL and cysteines in the A--sheet suggests that the RCL in active PAI-1 can be preinserted. ...
... Conclusion: formation of disulfide bonds between the cysteines in RCL and cysteines in the A--sheet suggests that the RCL in active PAI-1 can be preinserted. ...
Conversion of trypsin to a functional threonine protease
... group of Thr 195 in a position similar to that observed with Ser 195 in the native enzyme necessitates that the methyl group of the putative S195T substitution occupy a position that is sterically disallowed. In such a conformation, the methyl group of the substituting threonine would be 2.0 Å from ...
... group of Thr 195 in a position similar to that observed with Ser 195 in the native enzyme necessitates that the methyl group of the putative S195T substitution occupy a position that is sterically disallowed. In such a conformation, the methyl group of the substituting threonine would be 2.0 Å from ...
Redox regulation of cysteine
... its direct action is limited, and it would seem that the main reason for maintaining increased SOD activity is to prevent the formation of peroxynitrite, the reaction between superoxide and NO (Pacher et al., 2007). Catalase and peroxidases are enzymes that remove H2O2. Hydrogen peroxide is a produc ...
... its direct action is limited, and it would seem that the main reason for maintaining increased SOD activity is to prevent the formation of peroxynitrite, the reaction between superoxide and NO (Pacher et al., 2007). Catalase and peroxidases are enzymes that remove H2O2. Hydrogen peroxide is a produc ...
Characterization of Low Molecular Weight Glutenin Subunits by
... cysteines in parts of the molecule yet to be sequenced that make them chain extenders? This question can only be answered by future work, because almost no information about the arrangement of disulfide linkages in the gluten proteins exists despite the key role they play in determining the properti ...
... cysteines in parts of the molecule yet to be sequenced that make them chain extenders? This question can only be answered by future work, because almost no information about the arrangement of disulfide linkages in the gluten proteins exists despite the key role they play in determining the properti ...
Bread chemistry
... particularly glutamine. This amidebearing amino acid has a strong tendency to form hydrogen bonds between protein strands – a major factor in the physical structure and behaviour of gluten. In addition, the glutenin protein chains of the subunits contain thiol groups from the amino acid cysteine, wh ...
... particularly glutamine. This amidebearing amino acid has a strong tendency to form hydrogen bonds between protein strands – a major factor in the physical structure and behaviour of gluten. In addition, the glutenin protein chains of the subunits contain thiol groups from the amino acid cysteine, wh ...
Document
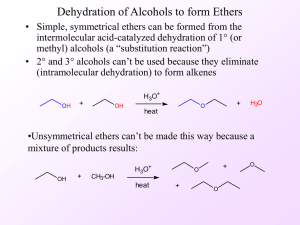
... • Blood alcohol level can be determined by having an individual blow into a tube containing K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, and an inert solid. • The alcohol in the exhaled breath is oxidized by the Cr6+ reagent, which turns green in the tube. • The higher the concentration of CH3CH2OH in the breath, the more Cr6+ ...
... • Blood alcohol level can be determined by having an individual blow into a tube containing K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, and an inert solid. • The alcohol in the exhaled breath is oxidized by the Cr6+ reagent, which turns green in the tube. • The higher the concentration of CH3CH2OH in the breath, the more Cr6+ ...
Chapter 8: Fibrous Proteins
... One of the difference between the many -keratin proteins is their Cys content The mechanical strength of horns, nails and skin depends upon the content of Cys residues and the number of disulfide bridges The more disulfide bridges the more rigid the resulting structure ...
... One of the difference between the many -keratin proteins is their Cys content The mechanical strength of horns, nails and skin depends upon the content of Cys residues and the number of disulfide bridges The more disulfide bridges the more rigid the resulting structure ...
Oxidation and Reduction of Organic Molecules
... number of rings in the original compound. • For example, if a molecule with a formula C8H12 was converted to C8H14 upon hydrogenation, the original molecule contains one bond and two rings. • Carbonyl groups (C=O) in a molecule can also undergo hydrogenation to form alcohols since they contain a ...
... number of rings in the original compound. • For example, if a molecule with a formula C8H12 was converted to C8H14 upon hydrogenation, the original molecule contains one bond and two rings. • Carbonyl groups (C=O) in a molecule can also undergo hydrogenation to form alcohols since they contain a ...
15_12_13rw
... 2) Final -e of alkane name is retained, not dropped as with alcohols. CH3CHCH2CH2SH CH3 3-Methyl-1-butanethiol ...
... 2) Final -e of alkane name is retained, not dropped as with alcohols. CH3CHCH2CH2SH CH3 3-Methyl-1-butanethiol ...
Disulfide formation in plant storage vacuoles permits assembly
... compost and vermiculite under greenhouse conditions at 15°C with a 16 hour light / 8 hour dark cycle. Prior to planting, seeds were imbibed in running water overnight. The development of Ricinus communis seeds is divided into seven stages (A to G) based on size, testa formation and state of hydratio ...
... compost and vermiculite under greenhouse conditions at 15°C with a 16 hour light / 8 hour dark cycle. Prior to planting, seeds were imbibed in running water overnight. The development of Ricinus communis seeds is divided into seven stages (A to G) based on size, testa formation and state of hydratio ...
PROTEIN SEQUENCING First Sequence
... III. Disulfide Bond Cleavage • Disulfides are reduced to thiol with dithiothreitol (DTT) or 2mercaptoethanol • Thiols are treated with alkylating agents (e.g. iodoacetic acid) to prevent the re-oxidation during subsequent steps. ...
... III. Disulfide Bond Cleavage • Disulfides are reduced to thiol with dithiothreitol (DTT) or 2mercaptoethanol • Thiols are treated with alkylating agents (e.g. iodoacetic acid) to prevent the re-oxidation during subsequent steps. ...
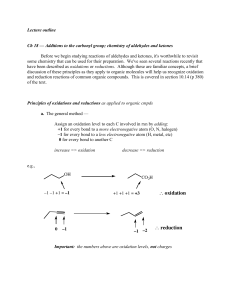
Wed March 3 lecture
... Ch 18 — Additions to the carbonyl group; chemistry of aldehydes and ketones Before we begin studying reactions of aldehydes and ketones, it's worthwhile to revisit some chemistry that can be used for their preparation. We've seen several reactions recently that have been described as oxidations or r ...
... Ch 18 — Additions to the carbonyl group; chemistry of aldehydes and ketones Before we begin studying reactions of aldehydes and ketones, it's worthwhile to revisit some chemistry that can be used for their preparation. We've seen several reactions recently that have been described as oxidations or r ...
Hmwk_4-09 Key
... sulfhydryl groups (Cys sidechains) e) O-Methyl isourea – is an electrophile that is easily attacked by the sidechain amino group of Lysine, to form homoarginine. The sidechain is therefore longer than that of either Arg or Lys, but has the same charge. It is no longer nucleophilic. The reaction is i ...
... sulfhydryl groups (Cys sidechains) e) O-Methyl isourea – is an electrophile that is easily attacked by the sidechain amino group of Lysine, to form homoarginine. The sidechain is therefore longer than that of either Arg or Lys, but has the same charge. It is no longer nucleophilic. The reaction is i ...
a short communication on formulation and evaluation of depilatories
... advantage that they do not have an appreciable odour but they tend to suffer from instability, forming stannates in the presence of water. A number of stabilizers, such as soluble silicates, triethanolamine, sugars, etc., were also tried but were not found to be effective and did not produce stable ...
... advantage that they do not have an appreciable odour but they tend to suffer from instability, forming stannates in the presence of water. A number of stabilizers, such as soluble silicates, triethanolamine, sugars, etc., were also tried but were not found to be effective and did not produce stable ...
E Reprint 212 - Trade Science Inc
... ABSTRACT Barium dichromate is used as an efficient oxidizing agent for the conversion of different types of thiols to their corresponding disulfides. Overoxidation does not occur and both aromatic and aliphatic thiols undergo oxidation in the same manner. 2006 Trade Science Inc. -INDIA ...
... ABSTRACT Barium dichromate is used as an efficient oxidizing agent for the conversion of different types of thiols to their corresponding disulfides. Overoxidation does not occur and both aromatic and aliphatic thiols undergo oxidation in the same manner. 2006 Trade Science Inc. -INDIA ...
Ribonucleotide Metabolism
... radical to that position. The hydroxide generated abstracts a proton from a second cysteine residue and leaves as water. The cysteine anion forms a disulfide bond with the adjacent cysteine residue passing a hydride to the C-2’ carbon complete the reduction at this position and shifting the radical ...
... radical to that position. The hydroxide generated abstracts a proton from a second cysteine residue and leaves as water. The cysteine anion forms a disulfide bond with the adjacent cysteine residue passing a hydride to the C-2’ carbon complete the reduction at this position and shifting the radical ...
102 Lecture Ch14b
... • Oxidation can also be defined as a loss of bonds to hydrogen • This is because H is less electronegative than all other nonmetals (besides P which is the same), so adds electron density to any element with which it forms a covalent bond • Thiols can be oxidized to disulfides using I2 (or Br2) • In ...
... • Oxidation can also be defined as a loss of bonds to hydrogen • This is because H is less electronegative than all other nonmetals (besides P which is the same), so adds electron density to any element with which it forms a covalent bond • Thiols can be oxidized to disulfides using I2 (or Br2) • In ...
Notes for using PROTPOL.f
... NSUB = no. of subunits (distinct from number of chains – all subunits must be equivalent. i. e., have the same number of peptides, aromatics, disulfides, Pro. A given subunit can consist of more than one chain and chains can and do generally differ in number of peptides, etc.) Ndis = no. of disulfid ...
... NSUB = no. of subunits (distinct from number of chains – all subunits must be equivalent. i. e., have the same number of peptides, aromatics, disulfides, Pro. A given subunit can consist of more than one chain and chains can and do generally differ in number of peptides, etc.) Ndis = no. of disulfid ...
Disulfide

In chemistry and biology a disulfide refers to a functional group with the general structure R–S–S–R. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or a disulfide bridge and is usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. In formal terms, the connection is a persulfide, in analogy to its congener, peroxide (R–O–O–R), but this terminology is rarely used, except in reference to hydrodisulfides (R–S–S–H or H–S–S–H compounds).In inorganic chemistry disulfide usually refers to the corresponding anion S22−, or −S–S−, for example in disulfur dichloride.