* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download d) Structural Proteins
History of molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Rosetta@home wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
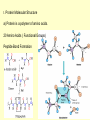
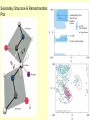
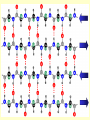
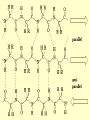
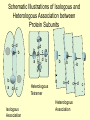
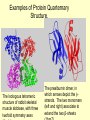
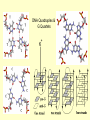
Protein structure Visualization Molecular Story Review “Central Dogma”: Sequence Structure function Sequence based analysis Structure based analysis Gene Sequence Function Protein Structure (Genomics) (Structural Genomics) Genomics) Sequence similarity Conserved domain Predict structure Predict function Primary Structure Secondary Structure Tertiary Structure Quaternary Structure Molecules Protein (Functional Protein - Protein Protein-DNA/RNA Protein-Lipids Protein-Small Bio-information data collection methods and major databases Genome sequencing Genbank (www.ncbi.nih.gov) Genechip gene expression database X-ray crystallography, NMR protein structure database ( www.pdb.org) 2D gel, mass spectrometry proteomics database Literature db PubMed (www.pubmed.org) Inherent genetic disease db OMIM (www.ncbi.nih.gov) Structure based analysis Molecular profile and story Protein structure: Primary Secondary Tertiary -Folding quaternary Protein structure determination: X-ray crystallography NMR spectroscopy Protein structure prediction: Secondary structure prediction Homology modeling Protein structure analysis: The structure character of the individual protein The structural basis of the protein function Protein family (based on conserved domain, motifs to predict their functions) Write the molecular profile and story I. Protein Molecular Structure a) Protein is a polymer of amino acids. 20 Amino Acids ( Functional Groups) Peptide Bond Formation c) The Secondary Structure and Tertiary Structure of Protein Elements of Secondary Structure: Helix β-Strand Loop Turn Helix β-Strand in β-Sheet Turn Loop Turn Secondary Structure & Ramachandran Plot Ramachandran Plot of CDC42-RhoGDI Complex [PDB Code 1DOA] Many alpha helices are Amphipathic 100 degree per residue Molscript Representations of Typical Protein Architectures. β 7 Propellor (2bbkH) β Barrel (2por) α 4-Layer Sandwich (2dnjA) Sandwich (2hlaB) Molscript Representations of Typical Protein Architectures. α β Barrel (4timA) α Helix Bundle (2ccy) 2 Solenoid (1tsp) α Horseshoe (1bnh) Schematic Illustrations of Isologous and Heterologous Association between Protein Subunits c d a b a b cd b a c d a cd--cd b b--a b a d c Isologous Association Heterologous Tetramer -b -d a---b c---d a---- a -b c---d Heterologous Association c - Examples of Protein Quarternary Structure. The Isologous tetrameric structure of rabbit skeletal muscle aldolase, with three twofold symmetry axes The prealbumin dimer, in which arrows depict the βstrands. The two monomers (left and right) associate to extend the two β-sheets DNA Quadruplex & G Quartets + K NMR Spectroscopy Sample-Spectrum-Structure Crystal X-Ray Crystallography Diffraction Electron Density Structure Protein Function and Structure (Architecture) a) Binding: Protein-DNA: transcription factors, eg TATA binding protein (PDB 1tgh) Protein-RNA: microRNA-target protein RNAi function Protein-small molecule: eg: Myoglobin-Heme/O2,Fe (PDB 1a6k) drug-target protein binding Protein-Protein: eg, chaperonin GroEL b) Catalysis: Enzymes Catalyzes biochemical reactions eg: DNA Polymerase catalyzes DNA replication (PDB 1pbx) HIV protease cleaves protein catalyzing the HIV replication (PDB 1a8k) c) Switching: eg: small GTPase Ras is a ‘Molecular switch’ for cell growth, GTP-bound, ‘ON’ (PDB 121p); GDP-bound, “off” (PDB 1pll) d) Structural Proteins: Silk: a stack of anti-parallel beta-sheets (PDB 1slk) within a sheet: covalent bonding and hydrogen bond, between sheets: Van der Waals force F-actin: helical assemblies of actin and actin-associated proteins muscle contraction, cytoskeleton The Second Project Go to www.pdb.org, a) Type a protein (or a disease) name, search for the structures b) Download the structure text file, save it as a text file with .pdb extension. c) Input the xxx.pdb file to Pymol (download from www.pymol.org) to see the molecular structure, notice its structural characters. d) Read the major reference paper (from www.pubmed.org) for this protein structure and the corresponding gene, summarize the connection of the structure and the protein function. Write the molecular story for this gene.