* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diagrams to Review 1
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Purinergic signalling wikipedia , lookup
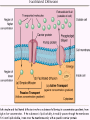
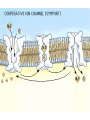
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
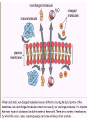
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
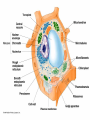
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
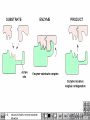
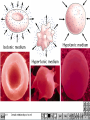
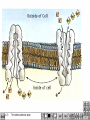
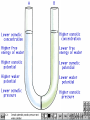
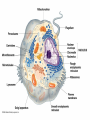
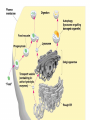
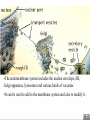
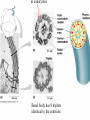
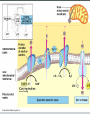
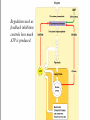
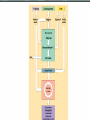
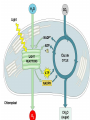
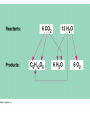
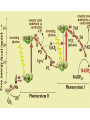
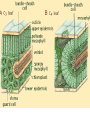
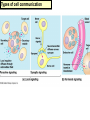
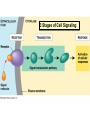
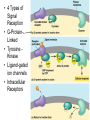
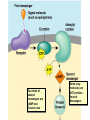
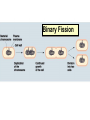
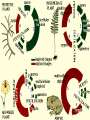
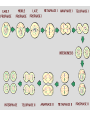
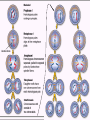
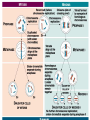
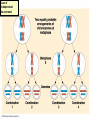
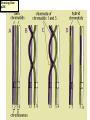
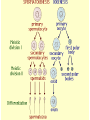
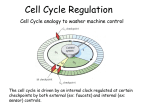
Two types of molecules make a fat Amino group Acid group R groups determine type of amino aci Animation 5.9.3 Product Reactant Reactant Product Negative change in free energy Animation 6.16 ATP helps to couple reactions By subdividing a large volume into smaller volume increase the SA/Vol ratio The surface area to volume ratio increases with smaller size •The endomembrane system includes the nuclear envelope, ER, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes and various kinds of vacuoles. •It can be used to add to the membrane system and also to modify it. Chloroplasts convert radiant energy from the sun into chemical energy the plant can use. Its inner membrane is composed of flattened sacs called thylakoids. A stack of these is called a granum. The thylakoid membrane have a green pigment called chlorophyll in them. Chloroplasts are part of a larger group of organelles called plastids. Leukoplasts are colorless and are used for storage (e.g. amyloplasts store starch). Chromoplasts have colored pigments. in eukaryotes Basal body has 9 triplets identical to the centriole NAD+ recycled NADox is recycled back to glycolysis Regulation such as feedback inhibition controls how much ATP is produced Types of cell communication 3 Stages of Cell Signaling • 4 Types of Signal Reception • G-ProteinLinked • Tyrosine Kinase • Ligand-gated ion channels • Intracellular Receptors Signal Transduction Pathways or Relay Molecules pass information INTO the cell Transfers a phosphate group from ATP to a protein To REVERSE the process, protein phosphatases remove the phosphate groups Usually serine or threonine is phosphorylated Two kinds of second messengers are cAMP and Calcium ions Some relay molecules are NOT proteins Second Messengers Page 199 Calcium can bind to Calmodulin Enzyme Cascade Effect amplifies the response Binary Fission MPF is only active when there is a high cyclin concentration MPF will phosphorylate many enzymes which will move the cell past the G2 checkpoint into M phase - it will also make a proteolytic enzyme that destroys cyclin and thus turn off MPF Cdk and Cyclin combine to form MPF - which is an active from of Cdk Law of Independent Assortment Crossing Over p236