* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 Chemical Bonding and Chemical Structure
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
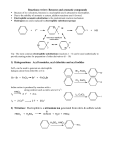
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
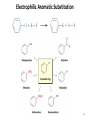
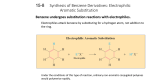
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
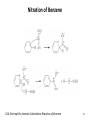
Vinylcyclopropane rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
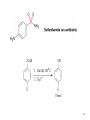
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
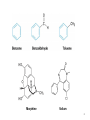
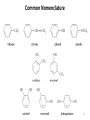
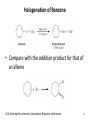
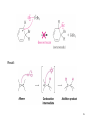
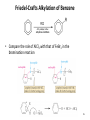
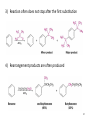
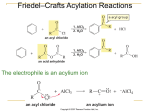
Chapter 16 The Chemistry of Benzene Derivatives Morphine Valium 2 Aromatic Hydrocarbons • Common sources: coal and petroleum • Physical properties: – Tend to be insoluble in water – MP’s relatively high – BP’s similar to molecules of similar structure and symmetry • Each additional C atom adds 20-30°C to the BP Common Nomenclature 4 IUPAC Nomenclature • Monosubstituted benzenes are named as other hydrocarbons, with –benzene as the parent name • Alkyl-substituted benzenes (arenes) are named in two ways: 1) If the alkyl group has 6 or fewer carbons, it is named as the substituent and the benzene ring is the parent 5 2) If the alkyl chain has more than 6 carbons, then the benzene ring is the substituent and is called a “phenyl” group • A phenyl group can be represented a few different ways • Don’t confuse a phenyl group with a benzyl group 6 • Disubstitued benzenes can be named in two ways: – Using o, m, or p – Using numbers 7 Nomenclature • Principle groups – If a substituent has highest priority, it is assumed to be on carbon #1 – If none of the substituents has priority over the others, cite them in alphabetical order 8 • Numbering is required when more than two substituents are present • Recall priorities: carboxylic acid > anhydride > ester > acid halide > amide > nitrile > aldehyde > ketone > alcohol (phenol) > thiol > amine 16.1 Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives 9 Problems • Name the following compounds: 10 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution 11 Halogenation of Benzene • Compare with the addition product for that of an alkene 16.4 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions of Benzene 12 Mechanism of Halogenation 16.4 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions of Benzene 13 Mechanism of Halogenation 16.4 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions of Benzene 14 Recall: 15 Three Mechanistic Steps in EAS 1. Generation of an electrophile 2. Nucleophilic reaction of the p electrons of the aromatic ring with the electrophile 3. Loss of a proton from the carbocation to form a substituted aromatic compound 16 17 Problem 1) Monobromination of toluene gives 3 products. Draw the entire mechanism for the formation of one product and draw the other two. 2) Draw the product(s): 18 Nitration of Benzene • Mechanism: 16.4 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions of Benzene 19 Nitration of Benzene 16.4 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions of Benzene 20 Reduction of Nitro-substituted Benzene Rings to Arylamines • Also works with SnCl2 21 Sulfonation of Benzene • Mechanism: 22 23 Problems 1) Draw the reactants required to produce the molecule below: 2) Draw the products for each step: 24 Friedel-Crafts Alkylation of Benzene • Compare the role of AlCl3 with that of FeBr3 in the bromination reaction 25 Limitations to Friedel-Crafts Alkylation 1) R must be an alkyl halide 2) The benzene ring cannot have amino or strongly electron withdrawing substituents 26 3) Reaction often does not stop after the first substitution 4) Rearrangement products are often produced 27 28 • Hydride Shift: • Alkyl Shift: 29 Problems • Give the products for the following reactions: 30