* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzymes/Macromolecules/Bonding
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
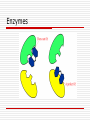
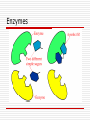
Enzymes/Macromolecules/Bo nding- covalent and ionic Enzymes Enzymes are proteins that help to speed up chemical reactions in the body Shape of Enzyme determines its function High temperature or extreme pH values may effect the shape of an enzyme molecule (denaturing). Makes enzymes useless Reaction Without-Enzymes Reaction With-Enzymes Enzymes are Specific An enzyme can be used for a specific reaction Double sugar needs to be broken apart Only one enzyme can function for this reaction Shape of an Enzyme can determine its functions Enzymes Enzymes Denaturing Denaturing Change in shape of enzyme due to high temperature or extreme pH Denaturing Irreversible process, enzyme will not work anymore Macromolecules Large Molecules Populate a cell and provide it with important functions of life Structural support Source of stored fuel Ability to store and retrieve genetic information Ability to speed biochemical reactions Four major types of Macromolecules Lipids Carbohydrates Nucleic Acids Proteins Polymers: chain of similar units or monomers, that are linked together by covalent bonds Four major types of Macromolecules Lipids Carbohydrates Nucleic Acids Proteins Diverse groups of molecules in Sugars nonpolymorphic Nucleotides form Amino Acids Proteins Chains of Amino Acids linked with Polypeptide Bonds 20 Amino Acids make Proteins, each differing only in the side chain Properties of side chains account for structural and functional differences Protein Carbohydrates Simple sugars called monosaccharides as well as large sugars called polysaccharides Glucose is hexose, a sugar composed of 6 carbon atoms, usually found in a ring form Starch macromolecule is a polysaccharide composed of 1000s of glucose units Carbohydrates Nucleic Acid DNA and RNA are nucleic acid Two polymers with complementary nucleotide sequence can pair with each other Pairing allows NA with the ability to Store Transmit Retrieve genetic information Nucleic Acid Lipids Triglyceride is composed of 3 fatty acid and 1 glycerol molecule Fatty acids attach to Glycerol by covalent ester bond Long hydrocarbon chain of each fatty acid makes the triglyceride molecule nonpolar and hydrophobic Lipids THANK YOU!