* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzymes - NVHSIntroBioPiper1
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Ultrasensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
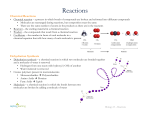
1. Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and ______. A. Oxygen B. Phosphorus C. Argon D. Nitrogen 2. Which organic molecule is used for transport and repair in the body? A. Lipids B. Proteins C. Carbohydrates D. Nucleic acids Warm-up Notes Organic Molecules Review Video / Demo Pepsin/Trypsin WS Vocab Clean-up Cool-down Quiz on Organic Molecules & Enzymes Thursday!! Guided Notes 6 Chemical reactions always involve the breaking of bonds in reactants and the formation of new bonds in products Reactants Products Activation energythe energy needed to get the reaction started Enzymes- Proteins that act as biological catalysts to speed up chemical reactions Identify many enzymes by the suffix –ase: helicase (unzips DNA) lactase (breaks down lactose) peptidyl transferase (forms peptide bonds in polypeptides) Enzymes speed up reactions Question: How do enzymes speed up reactions? Answer: They lower activation energy, making it easier for the chemical reaction to occur Enzymes are not used up in reactions Reactants + enzyme Products + enzyme Enzymes are very specific-they usually only work on one reaction Substrate-the material that the enzyme works on Active site-The special fold in the enzyme where the reaction happens Enzymes bind substrates (enzyme reactant) into active sites (pocket or groove on enzyme). While the enzyme and the substrate are joined, the enzyme catalyzes the reaction and converts the substrate to the product(s). • Catalyze chemical reactions: make them faster cofactor enzyme substrate chemical reaction Competitive Inhibition-When something besides the substrate blocks the active site Inhibitors— reduce the productivity of enzymes as seen to the right with herbicides. The body uses enzymes to control metabolic pathways. Non-competitive inhibition-When a molecule binds to another spot on the enzyme causing it to change shape and become inactive The most classic example an enzymatic reaction is the hydrolysis of sucrose (table sugar) into glucose and fructose. Another look… 1. Temperature 2. pH 3. Enzyme Concentration 4. Substrate Concentration Rate of Enzyme Activity is influenced by: Substrate concentration (more substrate = more activity until saturation) Temperature (higher temperature = more activity until the enzyme’s protein denatures) Rate of Enzyme Activity is influenced by: pH (usually in range of 6-8 for humans) Acidic Stomach Alkaline Intestine Inhibitors (reduce activity by binding or changing shape of active sites) Enzymes work quickly—about 1000 substrates are taken in and converted every second. Enzyme Video Review What type of organic molecule are enzymes? proteins How do enzymes speed up reactions? Lower activation energy The material that the enzyme works on is called the… substrate The location of the reaction on the enzyme is called the… Activation site What four factors affect enzymes? Temperature Ph Amount of enzyme Amount of substrate 1. 2. 3. Use a permanent marker to write your name on your bag. Word on blank side- definition on the lined side. Define 1. Acidthe following words: 8. Monomer 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Base Buffer Carbohydrate Lipid Nucleic acid Protein 9. Enzyme 10.Substrate 11.Active Site Divide your paper into 4. In each square, draw/write 1. Name: (Lipid, protein, nucleic acid, and carbohydrate) 2. Monomer: 3. Function/Job: 4. 2 examples: 5. Picture: 6. Any extra info from your notes/book Ch 2, pg 34-37 in your textbook for extra info. On your notecard, answer the following questions without using your notes. 1. Name at least 2 factors that affect enzymes. 2. What do enzymes do for the body? (ie. why do we need them?)