* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PROTEINS
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
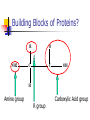
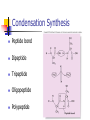
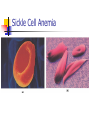
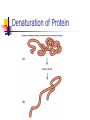
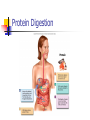
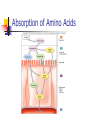
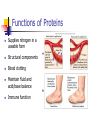
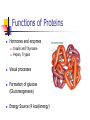
PROTEINS Chapter 7 Building Blocks of Proteins? NH2 R O C C OH H Amine group R group Carboxylic Acid group Examples of Amino Acids Essential versus Non-essential Limiting Amino Acid C is the limiting amino acid in this example CCCCC AAAAAAAA RRRRRR CAR CAR CAR CAR CAR R A A A Limiting Amino Acids Complementary Protein Food 1 CC AAAA RRR Food 2 CCCC AA RRR CAR CAR CAR CAR CAR CAR Dietary Aspects PKU = Phenylketonuria Vegetarian Diets Protein Synthesis Step 1: Step 2: Transcription Processing Step 3: Translation Transcription Formation of RNA from DNA template DNA= A C T G A T RNA= U G A C U A CODON #1 CODON #2 Condensation Synthesis Peptide bond Dipeptide Tripeptide Oligopeptide Polypeptide Levels of Protein Structure Sickle Cell Anemia Denaturation of Protein Turnover and Metabolism Protein Digestion Absorption of Amino Acids Functions of Proteins Supplies nitrogen in a useable form Structural components Blood clotting Maintain fluid and acid/base balance Immune function Functions of Proteins Hormones and enzymes Insulin and Thyroxine Pepsin, Trypsin Visual processes Formation of glucose (Gluconeogenesis) Energy Source (4 kcal/energy) RDA for Protein Promotes equilibrium 0.8 gm of protein / kg of healthy body weight 154 lb. = 70 kg 2.2 kg/lb. 70 kg x 0.8 g protein = 56 g protein kg healthy body wt Proteins in Foods Proteins in Foods Americans tend to eat more animal protein than plant protein (70%) There are many benefits to eating more plant proteins: Plant Protein No cholesterol Low in saturated fat High in (soluble) dietary fiber and phytochemicals HOWEVER: Somewhat less efficient (than animal protein) Lacking in one or more essential amino acid Protein-Energy Malnutrition Types of PEM: Kwashiorkor Marasmus Causes: Famine Anorexia Intestinal disorders Kwashiorkor Low protein density diet Energy needs are marginally met Subcutaneous fat is present Poor growth, edema, weakness, apathy, diarrhea, listlessness Marasmus Starving to death “skin and bones” appearance Insufficient protein, energy, nutrients Little or no subcutaneous fat Reduce brain growth Nutrition Perspective Vegan - primarily eats only plant foods Fruitarian - primarily eats fruits, honey, and vegetable oils Lactovegetarian - consumes plant products and dairy products Lactoovovegetarian - consumes plant products, dairy products, and eggs