* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Codon bias domains over bacterial chromosomes
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
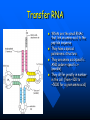
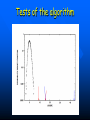
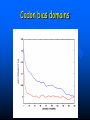
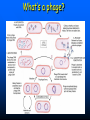
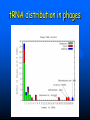
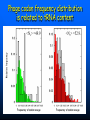
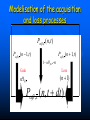
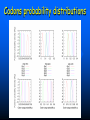
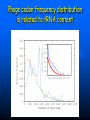
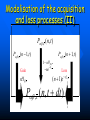
QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickT ime™ and a TIFF ( Uncompress ed) decompr essor are nee ded to see t his picture. Codon Bias and Regulation of Translation among Bacteria and Phages Thesis defense of Marc BAILLY-BECHET Advisor: Massimo VERGASSOLA Institut Pasteur, Dept Genomes & Genetics, Unit « In Silico » Genetics Summary Introduction to the bacterial translation system and the codon bias Structuration of the bacterial chromosomes by codon bias domains Why tRNAs in phages? Translation processes in prokariotuc cells Transfer RNA tRNAs are the small RNAs that link an amino-acid to the peptide sequence They have a special palindromic structure They are amino acid specific AND codon « specific » (wooble) They differ greatly in number in the cell (from ~100 to ~5000 for a given amino acid) Degeneracy of the genetic code Differential usage of synonymous codons at the genome scale Causes of the codon bias Non-selective causes of the codon bias Mutation biases (e. g. towards high/low G+C) Strand bias on the chromosome (GT bias) Selective causes of the codon bias: Translation efficiency Translation accuracy Codon-anticodon selection ? Codon robustness ? tRNA concentration correlates to codon bias Dong et al. (1996) J. Mol. Biol. 260:649 Codon bias domains over bacterial chromosomes Motivations of the project Aim: clustering the genes of an organism according to their codon bias Biological interests: – – – – Functional analysis of the groups of genes Role of codon bias in the chromosome structuration Comparison of the genome organization between species Inference of some codon bias causes from the classification Previous results Methods: correspondance analysis 2 main sub-groups of genes identified in multiple organisms: – Highly expressed – Horizontal transfer genes Methodological difficulties: – Choice of the number of groups – Choice of the distance Kunst et al. (1997), Nature 390:249 Key idea about the method: the optimization criteria Each group is defined by the probability distribution of codon usage generated by the genes it contains A good classification is one which maximize the gain of information on these probability distributions, relative to a uniform prior distribution max groupsamino acids * DKL Pprior || Ppost The clustering algorithm N N-1 ……. Threshold C =40 ……. Key idea about the method: selection of the number of groups The good number of groups is the one maximizing the average stability of genes attribution inside the groups, relative to the expected stability in absence of structure (random case) b s g Lg Cs Lg C s' s' S max b s1 s g C s 1 S Number of groups and clustering significance Codon usage inside the groups Qu ickTim e™ a nd a TIFF (Un compresse d) decompressor are need ed to see th is picture. Tests of the algorithm Gene function is correlated with codon bias 1. Highly expressed genes, translation and ribosomal proteins : COG J (9/22). 2. Unknown genes, pathogenicity islands and horizontally transfered genes : COG - (17/19). 3. Metabolism (synthesis & transport) : COG C (4/6), E (7/4) et F (7). 4. Membrane and carbohydrate metabolism genes : COG G (6) et M (3/3). 5. B. subtilis only -- Motility genes : COG N (5). Anabolic genes are grouped on the lagging strand Replication and transcription machineries collisions Anabolic genes are usually transcribed when no replication occurs => being on the lagging strand is not counter-selected. Codon bias domains Group by group analysis : influence of the GC% Group 2 GC=35.8% Group 4 GC=47% Acknowledgements (I) Frank Kunst and all the GMP Team Why tRNAs in phages? What’s a phage? Motivations of the project Understanding the presence of tRNAs inside bacteriophages – Correlation to the host or phage codon bias? – Differences between lytic and temperate phages? – Selection acting on tRNA acquisition and implications for phage evolution? Acquisition of tRNA sequences by bacteriophages Lysogenic phages are known to insert in microbial genomes in tRNA sequences => Imprecise excision could explain the acquisition of tRNA sequences Lytic phages cause liberation of the host genetic material after cell lysis => Acquisition of tRNAs sequences in the surrounding media or neighbour hosts Datas Beginning : – 200 DNA phage genomes, 23 hosts, 240 tRNAs Taken out : – Non sequenced hosts – Phages genomes without tRNAs – tRNAs inserted in prophagic regions – Phages having tRNAs their host do not have Final dataset : – 37 phages, 15 hosts, 169 tRNAs (6 duplicates, 1 triplet) tRNA distribution in phages Correlation of host and phages codon bias < R > = 0.77 0.27 real data < R > = 0.38 0.42 phage-random host => Codon usage is correlated between the host and the phage < R > = 0.83 0.14 real data - Temperate < R > = 0.61 0.39 real data - Lytic => The correlations are higher in temperate phages Phage codon frequency distribution is related to tRNA content <Nc> =49.9 <Nc> =52.9 First conclusions Lytic phages have a codon usage less similar to the one of their hosts when compared to temperate phages Lytic phages have more tRNAs than temperate ones Codon usage is more biased in lytic phages than in temperate ones Both seem to have tRNAs corresponding to the codons they use more Random uptake hypothesis tRNA content of host matches codon bias Codon bias of phage matches the host one’s => No need for the phage to have tRNAs ! Random uptake hypothesis: the tRNA content of a phage should be proportional to its host tRNA content, and so would be indirectly correlated to the codon bias of the phage Statistical tests of the random uptake hypothesis 1 f N N f (k) k1 1 f N N f (k) f (k) k1 Significance for high values of <f>: p = 0.68 – No specific enrichment in tRNAs for the phage high frequency codons Significance for high values of <∆f>: p < 0.0007 – Significant enrichment in tRNAs for the codons the phage uses more than its host Modelisation of the acquisition and loss processes P ,x (n,t) P ,x (n 1,t) 1 rH ,x n Gain Loss rH ,x P ,x (n 1,t) (n 1) P ,x (n,t dt) Inference of the parameters by maximum likelihood Probability Likelihood of the real data, given the model Maximum Most probable P(n) L(r) P(N ) , ,x likelihood r 0.060 Evolutive processes tested Selection based on: – Frequency of usage of the corresponding codon in the phage genome (+) – Frequency of usage of the corresponding codon in the host genome (-) – Difference of codon usage frequencies between phage and host genome (+) Duplication of tRNA on the phage genome Master model equation results Selection based on the phage frequency of codon usage is non significant (p=0.15) Selection based on the rarity of the codon in the host genome is slightly significant (p=0.018 before Bonferroni correction) Selection based on the difference of frequencies of codon usage between phage and host is highly significant (p<2.10-7) The tRNA duplication hypothesis has to be rejected Adaptative selection of tRNAs? Selection relative to the phage codon usage only could lead to a static tRNA content, and could be non-optimal after an host change Selection relative to the host codon usage only does not take into account the quick phage sequence evolution Selection needs to take both into account to be adaptative and gives rise to a useful tRNA content Conclusions Translational selection is a strong pressure acting on phage tRNA content tRNA content among phages is optimized to compensate for differences between host and phage codon usage This pressure is more important in lytic phages Acknowledgements (II) Massimo Vergassola Eduardo Rocha The committee members Yves Charon Guillaume Cambray Aymeric Fouquier d’Herouel All the family and friends who came today! Supp. Mat. Part 1 Codons probability distributions Tests of the algorithm (II) High CAI genes share the same codon bias: – 32/59 in group 1 of B. subtilis – 33/33 in group 1 of E. coli Genes in the same operon or pathway tend to belong to the same group Transcription and translation From Miller et al., 1970, Science 169:392 Translation regulation and synchronization by tRNA recycling Gene 1 Gene 2 Gene 3 Recycling phenomenon analysis On average, tRNA recycling should not increase translation speed Recycling could induce a coupling between close ribosomes, allowing for protein synthesis synchronization Synthetases are the limiting factor as they prevent in most cases a tRNA used by a ribosome to be re-employed by another close one Supp. Mat. Part 2 Phage codon frequency distribution is related to tRNA content Master equation model (I) Random excision P(n,t dt) (rH)P(n 1,t) (n 1)P(n 1,t) (rH n)P(n,t) t n (rH) rH lim P(n,t) e t n! Modelisation of the acquisition and loss processes (II) P ,x (n,t) P ,x (n 1,t) P ,x (n 1,t) 1 rH ,x nesf ,x Gain rH ,x Loss (n 1)e sf ,x P,x (n,t dt) Master equation models (II) Random excision P(n,t dt) (rH)P(n 1,t) (n 1)P(n 1,t) (rH n)P(n,t) t Random excision + selective loss P(n,t dt) (rH)P(n 1,t) (n 1)esf P(n 1,t) (rH nesf )P(n,t) t Random excision + selective loss + random copy P(n,t dt) (rH (n 1)c)P(n 1,t) (n 1)esf P(n 1,t) (rH n(esf c))P(n,t) t Selection is significant event relative to random hosts