* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration - Home - Mrs. Guida's AP Biology Class
Sulfur cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
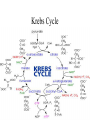
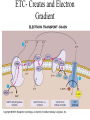
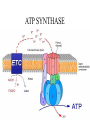
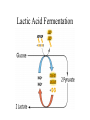
Cellular Respiration Chapter 7 Harvesting Energy • Autotrophs vs Heterotrophs • Cellular Respiration- the oxidation of organic compounds to extract energy from chemical bonds Getting Energy from Food • Digestion • Breaking bonds • Redox reactions – Dehydrogenations Electron Transport • Happens in stages…why important? • Aerobic vs anaerobic respiration • Electron Carriers 2 Steps in the oxidation of glucose • Substrate Level Phosphorylation • Oxidative Phosphorylation Overview of Aerobic Respiration Stages of Cellular Respiration • • • • Glycolysis Pyruvate Oxidation Krebs Cycle ETC and Chemiosmosis Products Of Glycolysis Glucose + 2 ADP + 2 P + 2 NAD+ 2 pyruvate + 2 ADP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 H2O Recycling NADH • Aerobic Respiration • Fermentation The Fate of Pyruvate Oxidation of Pyruvate to Produce Acetyl-CoA Pyruvate+ NAD+ + CoA acetyl-CoA + NADH + CO2 + H+ Krebs Cycle ETC- Creates and Electron Gradient ATP SYNTHASE • ETC and Chemiosmosis Energy Yield Actual vs Theoretical • 30 vs 36…why? Regulation of Aerobic Respiration • Feedback Inhibition • Figure 7.17 Oxidation without Oxygen • Methanogens use CO2 • Sulfur bacteria use Sulfate • Fermentation – Alcoholic – Lactic acid Alcoholic Fermentation Lactic Acid Fermentation Catabolism of Proteins and Fats • • • • Proteins to Amino groups Fatty acids to acetyl groups Intermediates of cellular respiration Figure 7.20 Evolution of Metabolism • • • • • • 1. Degrading Carbon Based Molecules 2. Glycolysis 3. Anaerobic Photosynthesis 4. Aerobic Photosynthesis 5. Nitrogen Fixation 6 Aerobic Respiration