* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gail`s powerpoint
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
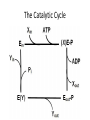
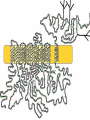
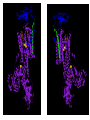
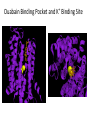
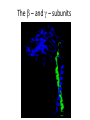
The + + Na ,K -ATPase Gail Virgin Introduction • Membrane Protein – Consists minimally of 2 subunits • Uses ATP to transport 3 Na+ ions into cell and 2 K+ ions out of cell • Converts 20 – 30 % of current ATP production in resting mammals to Na+ and K+ transport • P2-Type ATPase – Alkali metal cations – Pump gets phosphorylated during cycle • D-K-T-G-T-L-T The Catalytic Cycle Secondary Structures of the a-Subunit Mutational Anaylsis • D376A a-subunit mutant – Enzymatically inactive – Assembled with b-subunit and delivered to PM properly • Na pump does not need to be active in order to reach PM • All 3 glycosylation Asn replaced with Glu on b-subunit – Proper assembly and trafficking to PM with wild-type a-subunit – Catalytically active, but increased susceptibility to degradation • Mutants with one or more S-S bridge reduced on b-subunit – Enzymatically inactive – a- and b-subunits assemble properly – Heterodimer is retained in ER • Bridges provide stability • b-subunit lacking cytoplasmic domain – Properly trafficked to PM but inactive The Subunits • a - subunit – 1028 amino acids – 110 kDa – 10 transmembrane segments – 3 domains • A domain – Regulatory • P domain – Phospohorylated • N domain – ATP binding – 45% helical – 14% b-sheets • b - subunit – Unique to counter K+ transporting pumps – 305 amino acids – 55 kDa – 3 S-S bonds and 3 glycosylation sites – 16% helical – 16% b-sheets • g – domain – FXYD protein – 74 amino acids – Regulates pump in tissue- and isoform-specific manner – 35% helical Secondary Structures of the bsubunit and g-subunit Ouabain Binding Pocket and K+ Binding Site Magnesium and Asp376 The b – and g – subunits Cardiac Glycosides • Used to treat congestive heart failure • Inhibit the Na+,K+ATPase – Causes increase in intracellular Na+ levels – Slows down the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger – Increases intracellular Ca2+ levels – Results in stronger muscle contractions References • Kaplan JH. Biochemistry of the Na,K-ATPase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71:511-535, 2002 • Laughery MD, Todd ML, Kaplan JH. Mutational analysis of a-b subunit interactions in the delivery of Na,K-ATPase heterodimers to the plasma membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 278:34794-34803, 2003. • Ogawa H, Shinoda T, Cornelius F, Toyoshima C. Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump (Na+,K+-ATPase) with bound potassium and ouabain. PNAS. 106:13742-13747, 2009. . • Shinoda T, Ogawa H, Cornelius F, Toyoshima C. Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump at 2.4Å resolution. Nature. 459:446-451, 2009.