* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HG-6-64-1 in A375, HCT-116, HT-29
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
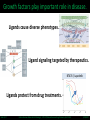
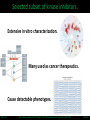
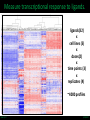
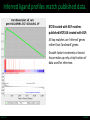
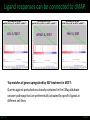
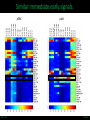
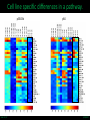
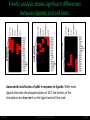
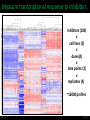
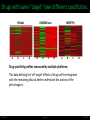
LINCS Consortium Meeting 10/27/2011 LINCS joint project: Linking the phosphoproteome and transcriptome in oncogenic signaling pathways. Mario Niepel and Peter K. Sorger Harvard Medical School Aravind Subramanian and Todd R. Golub Broad Institute Collaboration of the Broad and HMS LINCS Centers Slide 1/17 5/23/2017 LINCS joint project: a subset of perturbations. Collaboration of LINCS centers means that these perturbations are explored in great detail. • Time-points: series instead of one single time point • Doses: saturating and (multiple) subsaturating concentration. • Cell contexts: extensively characterized set of breast cell lines. • Multiple readouts: HTM, ELISA, RPLA, L1000, live-cell microscopy. Resulting data can be integrated into the larger LINCS effort: Cell lines are a subset of a set of 50+ breast cancer cell lines screened by HMS. Drugs are a subset of thousands of drugs screened by Broad Institute. Slide 2/17 5/23/2017 Growth factors play important role in disease. Ligands cause diverse phenotypes. Ligand signaling targeted by therapeutics. BT474 / Lapatinib Ligands protect from drug treatments. Slide 3/17 Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2, 127-137/Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 8, 627-644 5/23/2017 Selected subset of kinase inhibitors. Extensive in vitro characterization. Many used as cancer therapeutics. Cause detectable phenotypes. Slide 4/17 Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2, 127-137/Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 8, 627-644 5/23/2017 Measure transcriptional response to ligands. ligands(32) x cell lines (5) x doses(2) x time points (3) x replicates (4) ~4000 profiles Slide 5/17 5/23/2017 Inferred ligand profiles match published data. BT20 treated with EGF matches published MCF10A treated with EGF: All top matches are ‘inferred’ genes rather than ‘landmark’ genes. Growth factor treatments or breast tissue make up only a tiny fraction of data used for inference. Slide 6/17 5/23/2017 Ligand responses can be connected to cMAP. LCK: 1 / 5557 NTRK2: 3 / 5557 FRK: 5 / 5557 Top matches of genes upregulated by EGF treatment in MCF7: Queries against perturbations already contained in the CMap database uncover pathways that are preferentially activated by specific ligands in different cell lines. Slide 7/17 5/23/2017 Ligand families have specific response signatures. Correlation matrix of MCF10A Responses to ligand family members fall into specific clusters. There are specific differences in how a cell line responds to different ligand families. Slide 8/17 5/23/2017 Measure phosphorylation and expression responses. Measured signals cell lines / time points Ligands / concentrations Slide 9/17 5/23/2017 Similar immediate early signals. pERK Slide 10/17 pAkt 5/23/2017 Cell line specific differences in a pathway. pGSK3b Slide 11/17 pS6 5/23/2017 increasing sustained transient Kinetic analysis shows significant differences between ligands and cell lines. Automated classification of pAkt in response to ligands: While most ligands stimulate the phosphorylation of AKT, the kinetics of the stimulation are dependent on the ligand and cell line used. Slide 12/17 Evan Paull in Josh Stewart’s lab 5/23/2017 Computationally link proteome with transcriptome. Predictions of transcription factor and kinase activity: Using public databases, the activities of transcription factors and upstream kinases are predicated from the L1000 profiles for specific perturbations. Slide 13/17 Ma’ayan Lab 5/23/2017 Measure transcriptional response to inhibitors. Inhibitors (100) x cell lines (5) x doses(4) x time points (2) x replicates (4) ~16000 profiles Slide 14/17 5/23/2017 Proliferation response to HMS inhibitor library. Measurement of cell growth in response to drugs: High-throughput live cell microcopy is used to analyze the phenotypic responses (proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion) of cells to perturbagens. Slide 15/17 Benes Lab 5/23/2017 Drugs with same ‘target’ have different specificities. KiNativ a b c KINOMEscan d a b c MRCPPU d a b c d Drug specificity profiles measured by multiple platforms: This data defining the ‘off-target’ effects of drugs will be integrated with the remaining data to better understand the actions of the perturbagens. Slide 16/17 Gray Lab 5/23/2017 How do we apply this to biological questions. • How do changes in the proteome drive transcription? • How do responses of the proteome and transcriptome link perturbations with phenotypic outcomes? • Are these links cell type or tumor subtype specific? Do they correlate to drug responsiveness? • What are the similarities and differences in ligand responses across different ligands or different cells? • Can we learn more about how exogenous or autocrine/paracrine ligands effect drug responses? Slide 17/17 Ma’ayan Lab 5/23/2017