* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
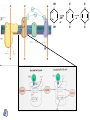
ELECTRON TRANSPORT SYSTEM Recaps Gycolysis glucose(C6H12O6) + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ 2 pyruvic acid(C3H4O3) + 2 ATP + 2 H2O + 2 NADH + 2 H+ Pyruvate dehydrogenase pyruvic acid + NAD+ + CoASH acetyl-CoA(C2H3O-CoA) + CO2 + NADH + H+ TCA acetyl-CoA(C2H3O-CoA) + 3 NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2H2O CoA-SH + 2 CO2 + 3 NADH + 3 H+ + FADH2 + GTP Overall Glucose (C6H12O6) + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ (cytoplasm) + 8 NAD+ + 2 FAD + 2 GDP + 2Pi + 2 H2O (mitochondria) + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ (cytoplasm) + 6CO2 + 8 NADH + 8 H+ + 2 FADH2 + 2 GTP (mitochondria) Much of the energy released by oxidation of glucose has been retained in bonds of reduced NADH and FADH2 Electron transport system Use oxidation of NADH + H+ and FADH 2 to form ATP and recycle NAD + and FAD Mitochondria Note: outer membrane, inner membrane, crista, matrix, intermembrane space Outer membrane permeable to > 1000 daltons Inner membrane impermeable to І 1 dalton (H+) Relevant enzymes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Electron transport and ATP synthesis as described in BIS 2A: reduced donor (e.g. malate) oxidized acceptor (NAD+) oxidized donor (e.g. OAA) reduced acceptor (NADH + H+) Why do electrons flow in this direction? 1/2 O2 H2O QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Mitochondrial electron transport chain: Electron flow depends on standard reduction potentials, since concentrations of carriers are ТfixedУ (except at the beginning and the end). Complex I: >30 polypeptides, 1 FMN, <7 Fe-S + centers, ~850 kD, proton pump pumping 4-6 H /2e Complex II: 4 polypeptides, 7 Fe-S centers, FAD, 100-140 kD, no proton pump Complex III: 11 polypeptides, 3 cytochromes, Rieske+ Fe protein, 240 kD, homodimer (500 kD); -2 H in,+ 4 + H out per 2e Complex IV: 13 polypeptides, 2 hemes, 2 Cu, 204 + kD; 2 H /2e O. | OH | | OH -2H+ -e- . O || -e- || O || O Summary: NADH and FADH 2 are oxidized by the ETS Energy released during e- flow is used to transport H+ across the inner mitochondrial membrane The gradient of H+ across the membrane represents a store of energy (to be used to make ATP)