* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aldehid dan Keton
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Aldol reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
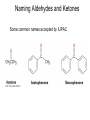
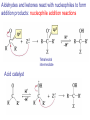
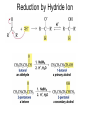
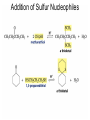
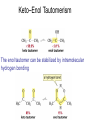
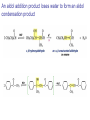
Aldehid dan Keton • Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) is common coenzyme • Hydrocortisone is steroid hormone secreted by adrenal glands • Penicillin G : an antibiotic Carbonyl Compounds Nomenclature of Aldehydes Naming Aldehydes and Ketones Nomenclature of Ketones Naming Aldehydes and Ketones Some common names accepted by IUPAC Boiling Points • More polar, so higher boiling point than comparable alkane or ether. • Cannot H-bond to each other, so lower boiling point than comparable alcohol. Carbonyl Structure • Carbon is sp2 hybridized. • C=O bond is shorter, stronger, and more polar than C=C bond in alkenes. Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones • Aldehydes from oxidation of primary alcohols using pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) • Aldehydes from reduction of carboxylic esters using diisobutylaluminum hydride (DIBAH) Aldehydes and ketones react with nucleophiles to form addition products: nucleophile addition reactions Tetrahedral intermediate Acid catalyst All carboxylic acid derivatives react by the same general mechanism The tetrahedral intermediate eliminates the weakest base Nucleophilic Addition Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition of H2O: Hydration Aldehydes and ketones react reversibly with water to give 1,1-diols, or geminal (gem) diols • Equilibrium favors carbonyl compound for steric reasons with the exception of formaldehyde Formation of a New Carbon–Carbon Bond Using Grignard Reagents Reduction by Hydride Ion Aldehydes and ketones react with a primary amine to form an imine This is a nucleophilic addition–elimination reaction The pH of the reaction must be controlled Aldehydes and ketones react with secondary amines to form enamines Water adds to an aldehyde or ketone to form a hydrate Addition of an Alcohol to an Aldehyde or a Ketone Addition of Sulfur Nucleophiles Oxidation of Aldehydes Tollens Test O R C H + 2 2 + Ag(NH3)2 + Ag(NH3)2 _ + 3 OH _ + 3 OH O H2O O H2O 2 Ag + R C O silver mirror _ 2 Ag + R C O _ + 4 NH3 + 2 H2O The reactivity of carbonyl compounds resides in the polarity of the carbonyl group in a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction The a-Hydrogen is Acidic the anion is stabilized by resonance Keto–Enol Tautomerism The enol tautomer can be stabilized by intramolecular hydrogen bonding One molecule of a carbonyl compound acts as a nucleophile and the other carbonyl compound acts as an electrophile Ketones are less susceptible than aldehydes to attack by nucleophiles An aldol addition product loses water to form an aldol condensation product The Mixed Aldol Addition