* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download today`s PowerPoint
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Aldol reaction wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
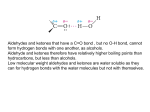
4.1.2 Carbonyl Compounds Syllabus points 4.1.2 a, b, e Aldehydes and Ketones; identifying their presence using Brady’s reagent (2,4-DNPH) Nomenclature iodopropanone 3-iodopentan-2-one 3-methylbutan-2-one ethanal 4-iodobutan-2-one ethanal 4-iodobutan-2-one propanal pentan-3-one pentanal Carbonyl Compounds • The functional group is the carbonyl group δ+ δ- C=O Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon, the electrons in the double bond tend towards the oxygen atom making it δ-. The carbon atom becomes δ+, making it susceptible to nucleophilic attack. See pi representation Q 1-4 pg 21 Aldehydes • The functional group of the aldehydes: H C=O R Where R are alkyl or aryl groups, and may or may not be different The aldehydes are named using the suffix -al E.g. CH2O methanal CH3CHO ethanal Ketones • The functional group of the ketones: R C=O R1 Where R and R1 are alkyl or aryl groups, and may or may not be different The ketones are named using the suffix -one E.g. CH3COCH3 propanone CH3CH2COCH3 butanone CH3CH2CH2COCH3 pentan-2-one Oxidation of carbonyls • What reagent is used to oxidise alcohols? • How do you know the alcohol has oxidised? • • • • • • Ethanol + [O] ? + ? Via distillation Ethanol + 2[O] ? + ? Via reflux 2-methylpropanal + [O] ? Propan-2-ol + [O] ? + ? Methylpropan-2-ol ? NB this year you WILL need to write redox equations using the actual reagents not just [O] Testing carbonyls Objectives • Describe the use of 2,4dinitrophenylhydrazine to detect the presence of a carbonyl group. • Identify a carbonyl compound from the melting point of the derivative. Tests for carbonyls • You can use 2,4 – dinitrophenylhydrazine or 2,4-DNP to test for the carbonyl group. • A solution of 2,4-DNP, methanol and H2SO4 is known as Brady’s reagent. • A positive test will give an orange/yellow precipitate. • Both aldehydes and ketones will test positively. No other compounds (e.g. Carboxylic acids or esters) will • The precipitate is called 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone derivative. • How would you know what type of carbonyl you have? • Overall reaction is given by the equation: • Look carefully at what has happened. Identifying a carbonyl • The yellow/orange derivative is slightly impure so the product is filtered and recrystallised to produce a purified crystal • The melting point of the crystals is then measured – this is used to identify the compound Compound Boiling point (°C) Melting point of 2,4-DNP derivative (°C) Heptan -2 -one 151 90 Cyclohexanone 156 162 Octan-2-one 173 58