* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Purinergic signalling wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Gap junction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
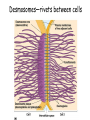
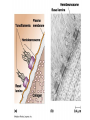
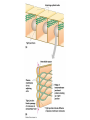
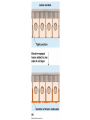
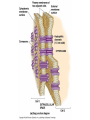
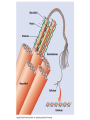
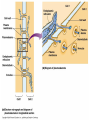
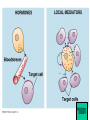
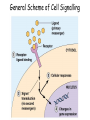
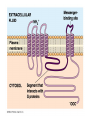
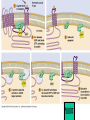
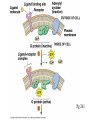
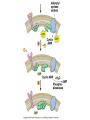
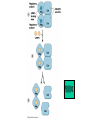
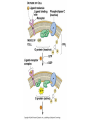
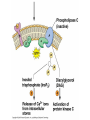
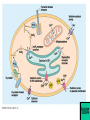
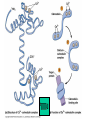
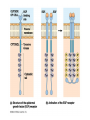
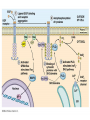
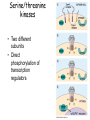
Cell-cell adhesion • Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) – Lots of them – Involved in many cellular processes • Cadherins – Adhesive glycoproteins Cell juctions • Adhesive junctions – Strong links • Tight junctions – Prevent leaks between cells • Gap junctions – Forms direct link between cells Adhesive junctions • • • • Desmosomes Hemidesmosomes Adherens junctions Focal adhesions All contain - intracellular attachment proteins—link to cytoskeleton - transmembrane linker proteins—link the cells Desmosomes—rivets between cells Adherens junctions • Belt around cell • Connects to actin, not tonofilaments • Look a lot like desmosomes • Found in – Heart – Epithelial layers • Oftern form belt • Called “focal adhesion” if connects to ECM Tight junctions Gap junctions • Direct electrical connection • Formed by connexons – Protein=connexin • Prominent in muscle and nerve—e.g. electrical tissues • Form of cell-cell communication Cell walls Plant cell walls • Cellulose (40%) • Branched polysaccharides – Hemicellulose (20%) – Pectins (30%) • Extensins--glycoproteins (10%) • Lignins—woody tissues – Insoluble aromatic alcohols – Cross-link to form wood Plasmodesmata Signal Transduction General Scheme of Cell Signalling Types of Receptors • G-protein linked receptors – cAMP – Ca2+ – Inositol triphosphate – Diacylglycerol • Protein-kinase receptors – Serine/threonine kinases – Tyrosine kinase G Protein linked receptors G proteins • Large heteromeric G proteins – Alpha—binds GTP/GDP – Beta – Gamma • Together they control the alpha subunit • Small monomeric G proteins – Generally called by another name – Example: ras Adenylate cyclase • Activated by G proteins • Makes cAMP • cAMP activates cAMP dependent protein kinase – aka protein kinase A (PKA) Pg 261 Diseases • Cholera – Vibrio cholerae – Toxin modifies a G protein – Continually activates adenylate cyclase • Whooping cough – Bordetella pertussis – Pertussis toxin – Inactivates a G protein that inhibits adenylate cyclase Inositol triphosphate and diacylglycerol second messengers Protein Kinase-associated Receptors Tyrosine kinase receptors • Activated by ligand binding – Often growth factors • Form dimers • Autophosphorylation – On tyrosines • SH2 domain – Src homology (domain) 2 region – Bind to phosphorylated tyrosines • Activate various second messengers Serine/threonine kinases • Two different subunits • Direct phosphorylation of transcription regulators