* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tight Junctions, Desmosomes, and Gap Junctions in Animal Cells
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
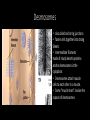
Tight Junctions, Desmosomes, and Gap Junctions in Animal Cells By Sonia Trejo and Hailey Scoggins Tight Junctions • At tight junctions the plasma membranes of neighboring cells are very tightly pressed against each Other. • Bound together by specific proteins (purple). • Form continuous seals around the cells to establish a barrier that prevents leakage of extracellular fluid across a layer of epithelial cells (see red dashed arrow). • tight junctions between skin cells make us watertight. Desmosomes • also called anchoring junctions • fasten cells together into strong Sheets • Intermediate filaments made of sturdy keratin proteins anchor desmosomes in the cytoplasm. • Desmosomes attach muscle cells to each other in a muscle. • Some “muscle tears” involve the rupture of desmosomes. Gap Junctions • also called communicating Junctions • provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to an adjacent cell • in this way they are similar in their function to the plasmodesmata in plants. • consist of membrane proteins that surround a pore through which ions, sugars, amino acids, and other small molecules may pass. • necessary for communication between cells in many types of tissues, such as heart muscle, and in animal embryos.