* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Extracellular components
Gap junction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
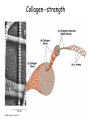
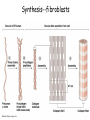
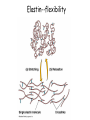
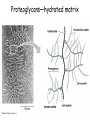
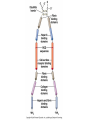
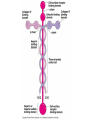
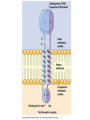
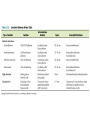
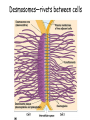
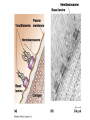
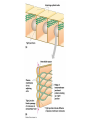
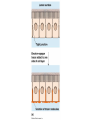
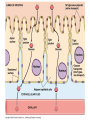
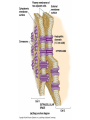
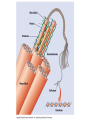
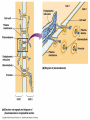
How do coated vesicles go to the right place and fuse with the right membrane? The “SNARE” hypothesis SNARE • Vesicle-SNAP-receptors (v-SNAREs) • Target-SNAP-receptors (t-SNAREs) • SNAP=soluble NSF attachment proteins • NSF=N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor Lysosomes • Digestive enzymes • Low pH (4-5) • Develop from late endosomes/hydrolases from Golgi • Activated by lowering the pH Extracellular components • Cell walls • Extracellular matrix – Bone – Cartilage – Connective tissue Types of molecules in ECM • Structural proteins—strength/flexibility – Collagen – Elastin • Proteoglycans--matrix • Adhesive glycoproteins—stick cells to matrix – Fibronectins – laminins Collagen--strength Synthesis--fibroblasts Elastin--flexibility Glycosaminoglycans Proteoglycans—hydrated matrix Adhesive glycoproteins • Extracellular – Fibronectins – Laminins • Cell surface – Integrins Fibronectins • Group of adhesive glycoproteins • 2 long linked proteins • Several binding domains Fibronectin roles • • • • Anchor cells to ECM Maintain cell shape Cell movement Blood clotting Laminins • Found in basal laminae – Special ECM – Under epithelial cells – Separates them from connective tissue • Role of basal laminae – Support – Permeability barrier • Contain – Type IV collagen – Proteoglycans – laminins Laminins • Very large proteins • 3 linked peptides • Multiple domains What binds the cells to the ECM? Integrins • Groups of transmembrane proteins • Link cytoskeleton to ECM • Fibronectin receptor is best known Cell-cell interactions Cell-cell adhesion Cell-cell communication Cell-cell adhesion • Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) – Lots of them – Involved in many cellular processes • Cadherins – Adhesive glycoproteins Cell juctions • Adhesive junctions – Strong links • Tight junctions – Prevent leaks between cells • Gap junctions – Forms direct link between cells Adhesive junctions • • • • Desmosomes Hemidesmosomes Adherens junctions Focal adhesions All contain - intracellular attachment proteins—link to cytoskeleton - transmembrane linker proteins—link the cells Desmosomes—rivets between cells Adherens junctions • Belt around cell • Connects to actin, not tonofilaments • Look a lot like desmosomes • Found in – Heart – Epithelial layers • Oftern form belt • Called “focal adhesion” if connects to ECM Tight junctions Gap junctions • Direct electrical connection • Formed by connexons – Protein=connexin • Prominent in muscle and nerve—e.g. electrical tissues • Form of cell-cell communication Cell walls Plant cell walls • Cellulose (40%) • Branched polysaccharides – Hemicellulose (20%) – Pectins (30%) • Extensins--glycoproteins (10%) • Lignins—woody tissues – Insoluble aromatic alcohols – Cross-link to form wood Plasmodesmata