* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELL MEMBRANE: Structure and Function
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
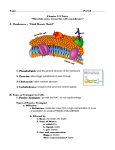
CELL MEMBRANE: Structure and Function Membrane Function: Supports cell contents by holding the cell together. Maintains cellular homeostasis by regulating what enters (food and nutrients) and leaves (waste). The fluid mosiac Membrane Structure: A phospholipid bilayer seperates the cell contents from the environment. Phophate is hydrophilic (water soluble) while lipids are hydrophobic (water insoluble). Embedded Carbohydrates act as chemical messengers attracting molecules like hormones to the cell. Embedded Proteins regulate the entry and exit of certain substances. Examples: nutrients, wastes, food. Membrane Permeablility Cell membranes will allow the passage of some molecules but not others. It is selectively permeable. Passive Transport Requires no energy because molecules move with the concentration gradient. High to low. Diffusion- solute molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion- protein passageways allow the movement of larger molecules through the cell membrane in accordance with the concentration gradient. Facilitated diffusion Osmosis- the movement of water from an area of higher to lower concentration… or the movement of water from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. Hypertonic vs. Hypotonic vs. Isotonic Osmosis Osmosis Active Transport- requires energy Requires energy because it moves against the concentration gradient from lower to higher concentration. Transport proteins- use energy to pump molecules into and out of the cell. Example: Sodium/Potassium pump Transport proteins/Molecular pumps Active vs. Passive transport Endo and Exocytosis- energy is used to engulf molecules, surrounding them with storage vesicles for later use or expelling them from the cell through the membrane. Endo/exocytosis CELL WALL Found around bacteria, fungi and plant cells. Rigid structure made of complex carbohydrates. Protects and supports the cell.