* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Toxic Pathways Less Traveled
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
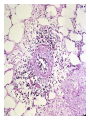
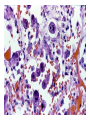
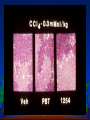
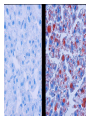
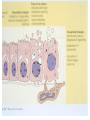
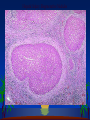
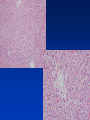
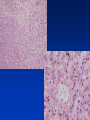
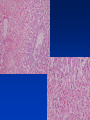
Cell Injury and the Pathogenesis of Human Disease (PATH 6226) “Cellular basis of disease” 200 years of observation: organ and microscopic May 2 and 4, 2011 Paul Boor M.D. SUGGESTED READING (PATHOLOGIC BASIS OF DISEASE, 8th EDITION) CHAPTER 1 Cellular Response to Stress and Toxic Insult; Adaptation, Injury, Death (pp 3-42) CHAPTER 3 Tissue Renewal, Repair, and Regeneration (pp 79-110) Rudolph Virchow (1821-1902) Cell Theory “Social Medicine” Cell Injury – General Considerations Numerous causes Biochemical events precede structural Duration and intensity of exposure important (direct dose/response relationship) Injury may be TISSUE (or cell) specific Injury depends of ability of cells to respond, resist, and repair injury Cell Injury – Causes Hypoxia / Ischemia Physical (mechanical, heat, radiation) Chemical Biologic Agents Immunologic (host) reaction Genetic derangement Nutritional imbalance, deficiency Cellular Degeneration Sublethal, usually reversible forms of cellular injury unassociated with severe cellular dysfunction. Oxidative Stress and Cell Injury Necrosis (or “Oncosis”) VS Apoptosis Types of Necrosis Coagulation Liquefactive Caseous “Fat” necrosis Liquefactive Necrosis Caseous Necrosis “Fat” Necrosis Key Words (Week 1 BBSC 6626) Anatomy of the hepatic lobule; Cell: Hepatocyte, Kupffer cell, bile ductules; Acetaminophen; Cytochrome p450s; imines; Reactive oxygen species; reactive nitrogen species; peroxynitrite; Adducts Hepatic Injury: Regenerative Nodules