* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell Cycle
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Acetylation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
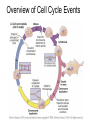
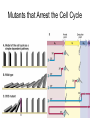
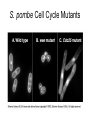
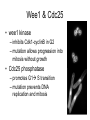
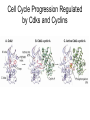
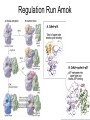
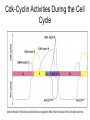
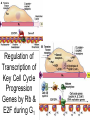
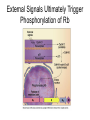
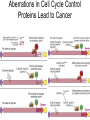
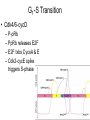
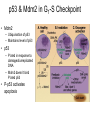
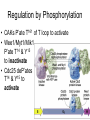
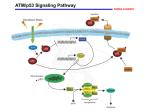
The Cell Cycle Overview of Cell Cycle Events Mutants that Arrest the Cell Cycle S. pombe Cell Cycle Mutants Wee1 & Cdc25 • wee1 kinase – inhibits Cdk1-cyclinB in G2 – mutation allows progression into mitosis without growth • Cdc25 phosphatase – promotes G1 S transition – mutation prevents DNA replication and mitosis Cell Cycle Progression Regulated by Cdks and Cyclins Regulation Run Amok • 18.1-Cdk2.mov Cdk-Cyclin Activities During the Cell Cycle G1-S Restriction Point Regulation of Transcription of Key Cell Cycle Progression Genes by Rb & E2F during G1 External Signals Ultimately Trigger Phosphorylation of Rb Aberrations in Cell Cycle Control Proteins Lead to Cancer G1-S Transition • Cdk4/6-cycD – P-pRb – PpRb releases E2F – E2F txbs CycsA & E – Cdk2-cycE spike triggers S-phase G1-S Checkpoint And S-Phase Considerations • Replication should not begin if DNA is damaged • DNA integrity monitored by – p53 induced genes • The p53 conundrum – too little – bad – too much - bad p53 & Mdm2 in G1-S Checkpoint • Mdm2 – Ubiquination of p53 – Maintains level of p53 • p53 – P’ated in response to damaged/unreplicated DNA – Mdm2 doesn’t bind P’ated p53 • P-p53 activates apoptosis S-Phase Controls • Replication must occur only 1 time / cell cycle • Origin “licensing” • ORC – origin recognition complex • SPF – S-phase promoting factor • Mcms – helicases that are only loaded once Regulation by Phosphorylation • CAKs P’ate T161 of T loop to activate • Wee1/Myt1/Mik1 P’ate T14 & Y15 to inactivate • Cdc25 deP’ates T14 & Y15 to activate Nuclear Localization of Cdk1-cycB1 Occurs at G2/M Transition • Cdk1 cytoplasmic , cyclinB1 shuttles, Cdk1-cycB1 shuttles • At end of G2 P’tion of CycB1nuclear export signal when complexed to Cdk1 – CycB1 carries Cdk1 into nucleus – Cdk1-cycB1 then trapped within nucleus – Activated by deP’tion of T14 & Y15 by Cdc25 Activation of Cdk1-cyclin Requires Inactivation of Cdk2-cyclinA G2 Checkpoint • Is DNA replication complete • Is DNA undamaged